Marine Engine Operations – Starting, Running, Stopping
For various types of main engines of ships, it is important to carry out proper checks, take necessary precautions and maintain parameters for trouble-free operation. Good watchkeeping and maintenance results in higher efficiency, fewer breakdowns, and smooth operation. In this article, we will go through some generalised and most important points for all types of main engines.
Preparing To Start Ship’s Main Engine
Before starting the main engine, the following checks and procedures are to be undertaken.
All components that have been overhauled are to be checked and wherever possible “function tested”. All equipment, tools, and rags used during overhaul are to be removed from the engine.
1. Air systems
a) Drain any water present in the starting air system
b) Drain any water present from the control air system at the receivers
c) Pressurise the air systems and ensure that the pressures are correct
d) Ensure compressed air is available at the exhaust valve ‘air spring’ closing cylinders
Related Read: 8 Things Marine Engineers Must Know About Starting Air System On Ship
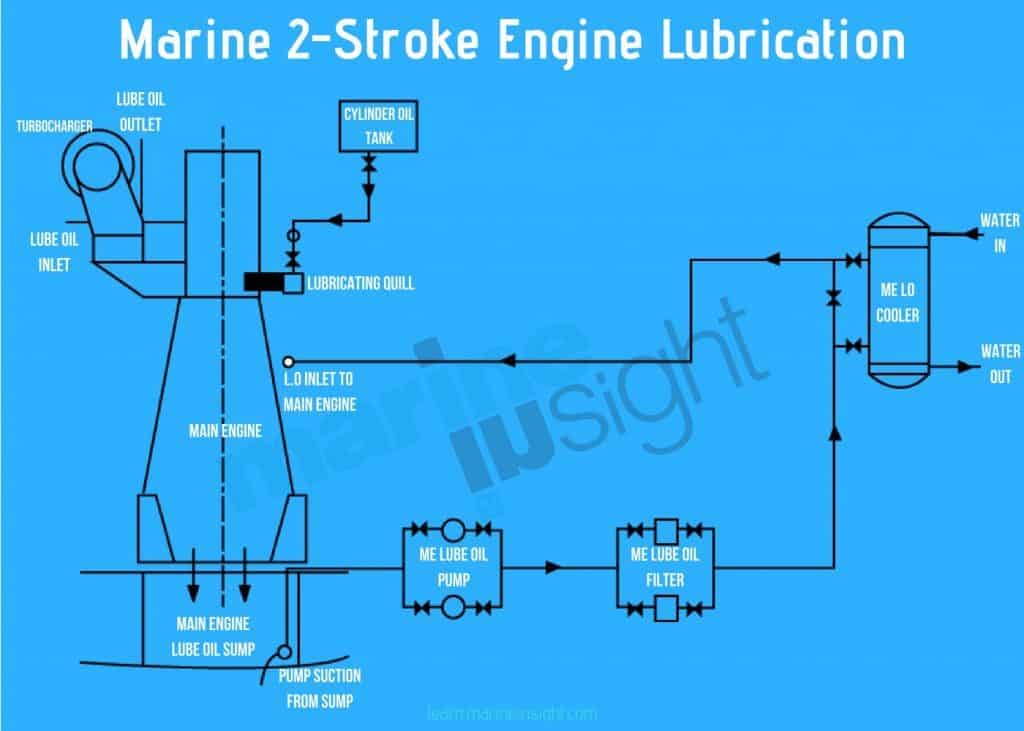
2. Lubricating oil systems
a) Check the oil level in the main engine sump and replenish if necessary
b) Start main engine LO pump and a turbocharger LO pump
c) Ensure all of the oil pressures are correct
d) Ensure there is adequate oil flow for piston cooling and turbochargers
e) Check the oil level in the cylinder LO tank and that the supply to the lubricator is open. Check cylinder oil flowmeter is properly functioning and note the counter of the flowmeter
Related Read: Ship’s Main Engine Lubrication System Explained
3. Cooling water systems
a) Ensure Main Engine Jackets are under normal circumstances, the main engine jacket water is continuously circulated through a preheater during the stay in port and are never allowed to cool down
b) Ensure that the cooling water system pressures are correct and that the systems are not leaking. Checks should be made again when the engine is at its correct operating temperature
c) Check the level of the expansion tank. An evident decrease in the water level of the expansion tank indicates leakage.

Related Read: General Overview of Central Cooling System on Ships
4. Slow turning the engine with the turning gear
Slow turning of the engine must be carried out to prevent damage caused by fluid leaking into any of the cylinders. Permission from the bridge must be sought before turning the engine. Pre-lubrication should be carried out. Always carry out the slow turning operation at the latest possible moment before starting.
a) Ensure the regulating handles are in the FINISHED WITH ENGINES position
b) Ensure all of the cylinder indicator cocks are open
c) Turn the engine one revolution with the turning gear. Check to see if fluid flows out of any of the indicator valves
d) Disengage the turning gear and ensure it is locked in the OUT position
e) Check that the indicator lamp for TURNING GEAR ENGAGED extinguishes
Related Read: How Marine Propulsion Engine of the Ship is Protected?
5. Slow turning the engine on starting air (blow through)
Permission must be sought from the bridge before turning the engine. The bridge should be asked for propeller clearance. Always carry out the slow turning at the latest possible moment before starting and within the last 30 minutes. Bring Main Engine to standby mode.
a) Select SLOW TURNING on the main engine operating panel if present or give a kick from the engine control room by moving the regulating handle to dead slow momentarily. When operating telegraph from engine control, communicate with the bridge, they should follow your command on the telegraph. As the engine turns, check to see if any fluid flows out of the indicator cocks
b) When the engine has turned one revolution, move the regulating handle back to the STOP position
c) Close all of the indicator cocks. Also, close the turbocharger drains
6. Fuel oil system
a) Check fuel oil supply pump and fuel oil circulating pump. If the engine was running on heavy fuel oil when stopped, the circulating pump and fuel heaters should still be running
b) Check the fuel oil pressures and temperatures. Check fuel oil flowmeters are properly functioning and note the counter of the flowmeter
Related Read: Fuel Oil Consumption Calculations For Ships
7. Miscellaneous
a) Check that all of the engine instrumentation is reading correctly. If not, check the instruments and replace as necessary
b) Check that all scavenge air receiver and box drains are open and that the test cocks are closed
c) Check that the engine top bracing system is in service
d) Check the thrust bearing temperature and lube oil pressure is in range. Check axial vibration damper and torsional vibration damper lube oil pressure is in range
e) Check the fuel leak off alarm is functional. Check the level of fuel leak off tank to notice any rise in level later due to leakage
f) Check the level of scavenge drain tank, the tank should not be full or else will lead to overflow of scavenge spaces of Main Engine
g) Check the governor is responding efficiently
Normal Operation Checks
- During normal running, regular checks have to be made and precautions are to be taken
- Regular checks of the system and engine pressures and temperatures
- The values read off the instruments compared with those given in the commissioning records, taking into account engine speed and/or engine power, provide an excellent datum for estimating the engine performance. Compare temperatures by feeling the pipes. The essential readings are the load indicator position, turbocharger speed, charge air pressure and exhaust gas temperature before the turbine. A valuable criterion is also the daily fuel consumption, considering the lower calorific value
- Check and compare between cylinders the mean indicated pressure, compression pressure and maximum combustion pressures
Related Read: Understanding Indicator Diagram and Different Types of Indicator Diagram Deficiencies
- Check the operation of the oil mist detector
- Check all of the shut-off valves in the cooling and lubricating systems for the correct position. The valves for the cooling inlets and outlets on each engine must always be fully open in service. They serve only to cut off individual cylinders from the cooling water circuit during overhauls
- When abnormally high or low temperatures are detected at a water outlet, the temperature must be brought to the prescribed normal value very gradually. Abrupt temperature changes can cause damage
- The maximum permissible exhaust gas temperature at the turbocharger inlet must not be exceeded
- Check the combustion by observing the colour of the exhaust gases
Related Read: What To Do When Black Smoke Is Coming Out Of Ship’s Funnel At Port?
- Maintain the correct charge air temperature after the air cooler with the normal water flow. In general, higher charge air temperatures will result in less oxygen in the cylinder, which in turn will result in higher fuel consumption and higher exhaust gas temperatures
- Check the charge air pressure drop across the air filters and air coolers. Excessive resistance will lead to a lack of air in the engines
Related Read: How Marine Air Charging System For Engines Has Changed Over Time
- The fuel oil has to be carefully filtered before being used. Open the drain cocks of all fuel tanks and fuel oil filters regularly for a short period to drain off any water or sludge which may have collected there. Maintain the correct fuel oil pressure at the inlet to the fuel injection pumps. Adjust the pressure at the injection pump supply manifold with the pressure-regulating valve in the fuel oil return pipe, so that the fuel oil circulates within the system at the normal delivery capacity of the fuel oil circulating pump
- The heavy fuel oil has to be sufficiently heated to ensure that its viscosity before the inlet to the fuel injection pumps lies within the specified limits
- Determine the cylinder lubricating oil consumption. Extended service experience will determine the optimum cylinder lubricating oil consumption
- The cooling freshwater pumps should be run at their normal operating point, ie, the actual delivery head corresponds with the designed value. If the pressure difference between inlet and outlet exceeds the desired value, the pump overhaul should be considered
- The vents at the uppermost points of the cooling water spaces must be kept closed
- Check the level in all water and oil tanks as well as all the drainage tanks of the leakage piping. Investigate any abnormal changes
- Observe the condition of the cooling freshwater. Check for oil contamination
- Check the charge air receiver drain manifold’s sight glass to see if any water is draining away and if so, how much
- Check the scavenge space test cocks to see if any liquid is flowing out with the charge air
- Check the pressure drop across the oil filters. Clean them if necessary
- The temperature of the running gear should be checked where possible by listening and observing the crankcase externally and monitoring the oil mist detector readings. Bearings that have been overhauled or replaced must be given special attention for some time after being put into normal service
- Listening to the noise of the engine will reveal any irregularities
- The power being developed by the cylinders should be checked regularly and adjustments made via the control system to preserve cylinder power balance
- Centrifuge the lubricating oil. Lube oil samples should be taken at frequent intervals and sent ashore for analysis
- Check the exhaust valves are rotating and operating smoothly. If not, the valve not rotating normally has to be overhauled at the next opportunity
Securing After Stopping
- After Bridge has given Finish with Engines, switch the engine control to the engine control room
- Check that the auxiliary blowers switch off automatically at Finish with engines(FEW) if they are in AUTO mode or else switch them off manually
Related Read: How to Tackle Low Load Operating Conditions of Marine Engine?
- Close the starting air valve of the main engine and vent control air system. A good practice is to lock the main starting valve in its lowest position by means of the locking plate
- Close the valve for starting the air distribution system
- Engage the turning gear and check the indicator lamp
- After stopping the engine, wait a minimum of 15 minutes before stopping the main engine LO pump if work is to be undertaken in the crankcase. This prevents overheating of cooled surfaces in the combustion chambers and counteracts the formation of carbon deposits in the piston crowns
- Keep the engine preheated to a minimum of 50°C or according to the main engine manual requirement
- If the engine was operating on HFO, do not stop the FO circulating and supply pumps. If the engine was operating on MDO, both the FO circulating and supply pumps may be stopped
- Switch off any equipment which is not required during the engine standstill period
You may also like to read – Free Sample:Generator Running Tests
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of Marine Insight. Data and charts, if used, in the article have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and Marine Insight do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendation on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and Marine Insight.
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Subscribe To Our Newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.




Can I take part of your article for my studying program in college? (Securing After Stopping)
Hi Alex,
You can if it is for educational and non commercial purpose. You need to provide credit to the author and https://www.marineinsight.com