A Guide To Marine Gas Oil and LSFO Used On Ships
The mega marine engines of ships burn tonnes of fuel every day in order to propel massively loaded ships. These engines are known to use low-grade fuel oil to lower ship operating costs as cost of fuel represents as much as 30-50% of total operating costs of a ship.
Unfortunately (or fortunately), it’s not always possible to use low-grade fuels such as heavy fuel oil or HFO in regulated areas known as ECAs or Emission Control Areas. Marine Gas Oil Fuel or MGO is one of the most prominently used clean fuel in such cases.
Related Read: Download FREE eBook – A Guide to ECA Compliance For Ships + 4 Bonuses
Understanding Marine Gas Oil
The shipping industry is amongst the “early-adapters” in the transportation sector to develop and follow stringent environmental laws in order to move cargo worldwide. Fighting air pollution from ships has been the top agenda for the Marine Environmental Protection Committee, and hence several regulations have been enforced to curtail the harmful emissions from ships such as Sox and NOx.
Related Read: Marine Pollution by Ships -Tips for Reducing & Recycling Waste at Sea
With the ever-changing technology on ships, the fuel that is used to run marine engines is also changing rapidly. Recently, LNG is being seen as the “future fuel” for the shipping industry, however, the industry as a whole is yet to adapt to this change, and thus Marine Gas Oil is still one of the most preferred clean fuel used on ships.
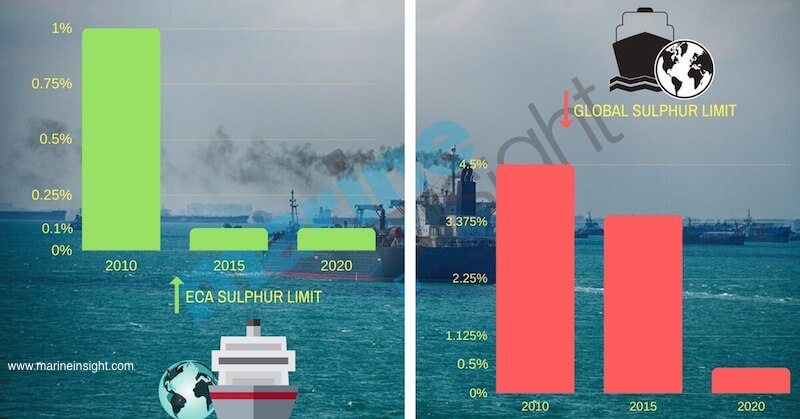
Sulfur Content in Marine Gas Oil
Marine Gas Oil used on ships is a blend component of the light cycle (gas) oil (LCGO) that contains about 60% aromatics. Due to the high aromatic nature, the density of a marine gas oil blended with LCGO will be higher than the gas oil from an atmospheric distillation refinery. The density of MGO will usually be closet to 860 kg/m3 (at 15°C).
Sulfur Content and Cetane Index
The marine gas oil is also considered as low sulfur fuel oil or LSFO because it has sulphur content between approx. 0.10 and 1.50 m/m %.
Related Read: FAQs: Sulphur Limits In Emission Control Areas
Types of clean fuel oil for the maritime industry available in the market:
- Residual marine or RM fuel oil is a type of diesel oil which needs heating for usage
- Distillate marine or DM fuel oil, which does not require any pre-heating for usage. It can further be classified as DMA fuel which is clear and brighter in appearance; DMB and DMC marine diesel oil grades which are not required to be clear and bright.
The RM and DM are types of marine oils, which can be further divided into groups, depending upon the sulphur content in the marine fuel oil.
– LSFO: Products that are above 0.10% but meeting a 0.50% sulphur limit
– ULSFO: Product with maximum of 0.10% sulphur content
Nowadays, the new age ULSFOs in the market typically have only 10 to 15 parts per million (ppm) sulphur or 0.001% to 0.0015%.
Cetane index is one of the essential marine fuel oil properties only applicable to marine gas oil and distillate fuels. It defines the ignition quality during the combustion process in a diesel engine. The cetane index is calculated from the Cetane number of the fuel which is provided in the “property of marine fuel details” in bunker delivery note.
Related Read: Ways to Achieve Efficient Combustion in Marine Engines
In general, the higher rpm engine requires high cetane index fuel. A low cloud point gas oil may only be stored onboard in drums because of its low flashpoint.
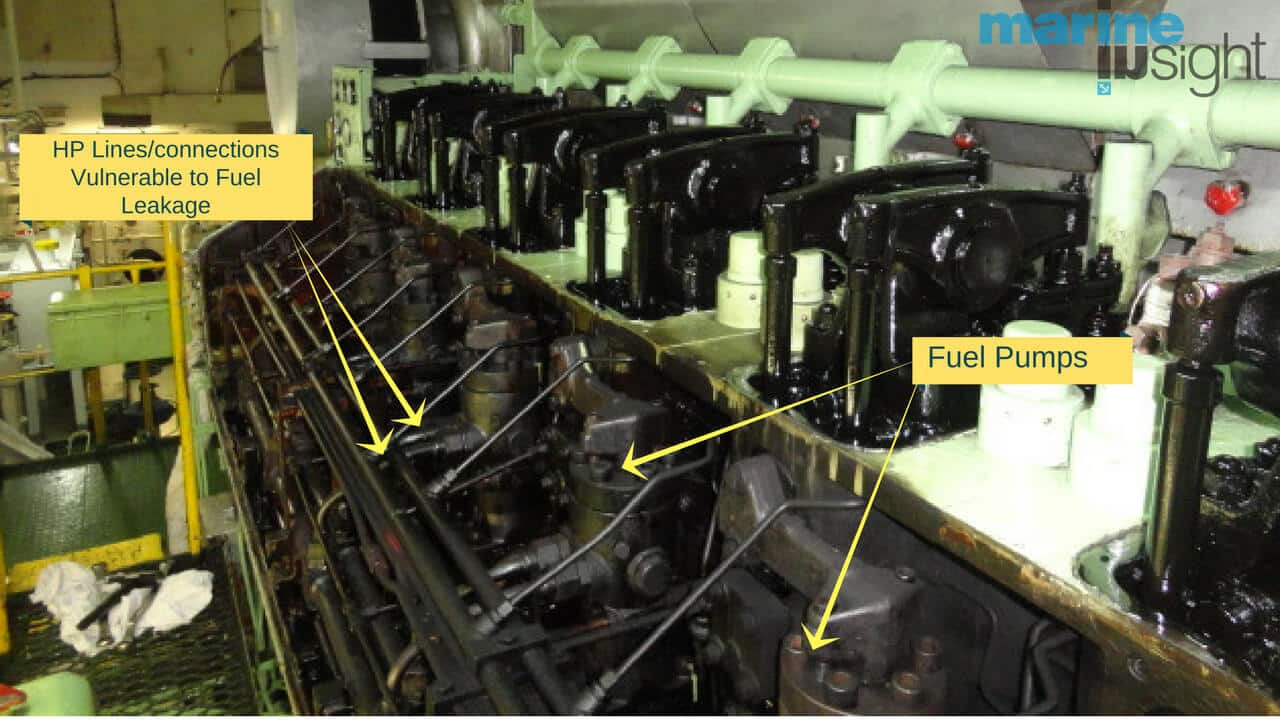
General Problems Associated with MGO
Microbial contamination, caused by bacteria and fungi, occurs in a fuel having water quantity. Due to bacterial presence, the fuel systems will generate problems such as chocked fuel filters and erratic engine operation. Possible microbiological contamination indicators are:
– Hazy appearance on the oil surface
– Suspended impurities in the oil
– Presence of the emulsion or a slimy interface layer between water and gas oil
– Foul smell from the tank drain with slight sludge discharge during draining operation
Fuel pumps of marine engines are designed for a minimum viscosity. The viscosity of Marine Gas Oil is very low as compared to the pump design factor which leads to inadequate hydrodynamic lubrication, causing wear and scuffing.
Related Read: Viscosity Meter and Viscosity Controller Used on Ships
A decrease in fuel viscosity may cause an increase in fuel leakage between the pump plunger and barrel.
The leakage can lead to a hot start, and low fuel setting starts difficulties, especially in worn fuel pumps.
Due to the low viscosity of the marine gas oil, the external and attached fuel pumps may not deliver the fuel at the required pressure, which will eventually hamper the designed power output of the engine.
Burning MGO in 4 stroke engine
The diesel generator installed on ships these days operate on both residual and distillate fuel. The valve seat deposits (on the inlet valve) is significantly less when using distillate fuel as compared to using residual fuel oil. This is because the distillate fuels such as Marine Gas Oil produces fewer combustion deposits.
The 4 stroke marine engine efficiency on the ship is measured on the basis of residual oil, and the design of the engine is done focusing on the use of residual fuel. Most of the 4 stroke engines are installed with water-cooled injection nozzles to reduce the injector tip temperature (for avoiding coking of the fuel which would cause deposits known as trumpets on the nozzle tip).
When using distillate fuel, the nozzle cooling arrangement will further reduce the temperature of the distillate fuel, already having very low viscosity. The additional cooling with water may also cause overcooling of nozzle, leading to falling of temperature below the dew point of the sulphuric acid in the combustion gas and cause corrosion of the nozzle. To tackle this, the engineer must ensure to turn off nozzle cooling during distillate marine fuel oil operation.
Related Read: Important Generator Design and Operational Features Ship Engineers Must Know
Another problem associated with the usage of marine gas oil is leakage. As the viscosity of the fuel is much lower than the regular fuel of the engine, it accelerates the fuel leakage from pumps and also contaminates the lubrication.
To tackle this problem, most of the 4 stroke engines comes with lubricating sealing oil at the fuel pump. This oil seals the passage of distillate fuel to minimise the leakage.
Related Read: Situations When Ship’s Generator Must be Stopped Immediately
Most of the residual fuels are not compatible with sealing lubricating oil, hence the engineer must ensure to switch off the sealing oil to avoid compatibility issues, else it will lead to problems like fuel pump sticking etc.
During the burning of low sulphur fuel oil or LSFO, lacquering in liner may also be observed. Marine gas oil produces deposits which stick on the liner surface and disturbs the oil film lubrication in the liner. The engine design and use of aromatic fuels as the primary burning fuel are important factors that can contribute to increasing the lacquer formation.
The BN of the lube oil used in 4 stroke engines that operate majorly on distillate marine fuel oil is in the range of 10 to 16 mg KOH/g. When the engine is operated with residual fuels, the BN of the lubricating oil is kept between 30-55 mgKOH/g.
When using distillate fuel for a more extended run (more than 1000 hours), it is always advisable to switch the lube oil with lower Total Base Number (TBN) with value as stated above. For shorter operation, it is not critical for the engine to keep using lubricating oil with BN of 30-55 mg KOH/g.
Related Read: Fuel Oil Change Over Procedure for Ship’s Main and Auxiliary Engines
Burning MGO in 2 Stroke Engine
- The 2 stroke engines operate typically under heavy fuel oil outside the ECAs and before entering the Emission Control Areas they switch over fuel from HFO to LSFO.
- During the switchover process, there is a mixing of heavy fuel oil with a low aromatic hydrocarbon distillate fuel. This increases the risk of two incompatible fuels burning inside the engine cylinder, causing the asphalt of the heavy fuel to precipitate as heavy sludge and leading to filter clogging
Related Read: Why 2-stroke Engines are Used More commonly than 4-stroke on Ships?
- As the names suggest, LSFO produces a negligible amount of sulphuric acid, and hence if the correct TBN lubricating oil is not used, the alkaline components produced in the cylinder will not be neutralised. This will potentially harm the liner and other parts of the combustion chamber. These alkaline deposits will lead to the removal of cylinder oil film causing contact of metal to metal parts between liner and piston rings and resulting in scuffing and seizure of the engine.

- The engineer operating the marine engine must ensure to switch to lubricating oil of LOW TBN when switching to LSFO and vice versa when using heavy fuel oil
- Leakages during the running operation of MGO or LSFO is another problem experienced in 2 stroke marine engines. This is because the viscosity of MGO is lower than that of HFO.
Related Read: Understanding Hot And Cold Corrosion In Marine Engines
For new marine engines running on heavy fuel oil, the engineer officers have to evaluate the cylinder conditions and report to the engine maker after changing the fuel to LSFO to check the deposits and scuffing on combustion chamber parts such as piston, crown, liner, and ring.
Responsibilities of ship staff While receiving Marine Gas Oil
- While receiving the LSFO during bunker operation, check the bunker delivery note to ensure the quality of the oil meets the main and auxiliary engine manufacturers’ fuel oil specifications
- During the bunkering operation, the ship’s staff has to ensure to set the bunker line carefully so as not to mix the receiving marine gas oil with different grades present onboard
- It is always advisable to use an empty tank to receive marine gas oil or receive the MGO in a tank which is filled with a similar grade.
- Ensure the ship management office works with bunker supply staff when ordering correct grade and ISO standard fuel with required sulphur content for ECA use
- A de-aerating arrangement during bunker operation will remove the airwaves entering the bunker tank which may affect the bunker quantity
Related Read: 13 Malpractices In Bunkering Operations Seafarers Should Be Aware Of
The contamination of fuel can happen at any part of the supply chain, i.e. at Fuel-producing companies, when the fuel is with dealers, or at the end-users. It’s a collective responsibility of all to avoid contamination.

Hence the sample must be sent to shore laboratory as soon as the bunker is received on the ship
Onboard Care
- Ensure the gas oil storage does not contaminate from water ingress. Thus, it is important to maintain good water draining and housekeeping.
- Check filters of the fuel line when distillate fuel is in use
- Check the water content of the fuel and ensure the sample is sent to shore lab to check for lube oil and microbial contamination etc. at regular intervals of time
- Whenever necessary, drain the tanks which are filled with MGO
- When using distillate fuel in the marine generator, ensure to switch off nozzle cooling water to avoid overcooling of injector nozzle.
- The crew should have excellent knowledge on the changing-over procedure from HFO to LSFO when entering ECA and vice versa with the minimum possibility of mixing of fuels to avoid non-compatibility issues
- During the changeover process, care must be taken to monitor the temperature of the fuel system and when the HFO is changed to LSFO and vice versa, the viscosity within the system must not drop below 2 CST or exceed 20 CST.
- The company has to ensure all the technical requirements are in place when using LSFO or marine gas oil. If the ship is plying the first time into the ECA, the company should revise fuel oil management procedures to ensure the crew has prior knowledge of HFO to LSFO changeover and low TBN lube oil for the main engine etc.
- The bunker storage tanks used for marine Gas oil or low sulphur fuel oil should be cleaned regularly to keep them free from sludge, which cannot be drained during normal operation.
Related Read: Important Points To Consider While Cleaning Tanks On Ships
The engineer must ensure correct fuel oil viscosity, and fuel pump pressure is maintained when the engine is running on marine gas oil.
Most of the diesel fuel does not require pre-heating (Distillate Marine fuel). Maintain the correct temperature if Residual Marine fuel is used.
For the marine engine efficiency, it is essential to maintain the fuel viscosity when running on marine gas oil. Marine gas oil or MGO Cooler/ chiller can be installed in the FO feed pipeline to control the viscosity.
Related Read: Ways to Monitor and Measure Marine Engine Performance
Even with the advantage of low emission from ship’s engine, LSFO or ULSFO has few disadvantages i.e. not compatible with the current engines the ships are using.
The problems arising due to marine gas oil may lead to severe catastrophes such as engine failure (due to fuel pump problem or seizure of combustion chamber parts), resulting in vessel collision, grounding and marine pollution. It is therefore important for the ship’s crew to know the pros and cons of these fuels and follow the correct procedure when handling such fuels onboard ships.
Disclaimer :
The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data or profits arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this website.
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Latest Shipboard Guidelines Articles You Would Like:
Disclaimer :
The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data or profits arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this website.

About Author
An ardent sailor and a techie, Anish Wankhede has voyaged on a number of ships as a marine engineer officer. He loves multitasking, networking, and troubleshooting. He is the one behind the unique creativity and aesthetics at Marine Insight.
Daily Maritime News, Straight To Your Inbox
Sign Up To Get Daily Newsletters
Join over 60k+ people who read our daily newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.







what all problems will be faced with 2 oil purifiers connected together in the system
Running 2 purifier in parallel is known as batch purification system used for treating large quantity of fuel. If set-up properly, it won’t give any issues.
To what database/source did you use in stating the sulfur limits for the different fuel types? Thank you!
Let us alleviate Marine Gas Oil Shortage faced by the Shipping Industry.
Thanks for explaining that the diesel generators on machine ships use both residual and distillate fuels. I’ve been interested in learning more about the fuels that marine ships have delivered to them. I’m glad I read your article and learned about the different types of fuels that machine diesel generators use.
@Daphne: We are glad that the information in our portal came handy to you. Please check this article which may be of your interest as well-
https://www.marineinsight.com/tech/marine-heavy-fuel-oil-hfo-for-ships-properties-challenges-and-treatment-methods/
Hi there,
Can you specify the properties of MGO (prior to the fact about its 60% content of aromatics). I would like to know what MGO consists of in general.
I hope you can help. Thank you in advance!
Best wishes,
Jacob
Can you mention some of the solutions related to the disadvantages using the LSFO and MGO that can make the operation of the ship using that type of fuel more efficient ?
Thanks for explaining
How much TBN of engine oil can drop in new marine engine oils?
Thank you
WHAT ARE THE RANGE IN TEMPERATURE OF LSFO WHEN IT IS IN PURIFYING SYSTEM AS WELL AS LUBE OIL? THANKS FOR THE INFO 🙂
45m motor yacht with 2 x 1.000Kw Mitsubishi main engines and 100Kw Gen sets. Is AGO preferable to MGO in our case?
What are the Pros and Cons of these 2 fuels in our case? Thanks
AGO (Automotive Gas Oil) and MGO (Marine Gas Oil) are both types of diesel fuel, but MGO typically has a higher sulfur content and is used specifically for marine vessels. The main advantage of using AGO instead of MGO in your 45m motor yacht would be that AGO typically has a lower sulfur content and thus may be more environmentally friendly. However, AGO may be more expensive than MGO and may not be readily available at all ports, so it is important to consider the cost and availability of the fuel when making a decision.