What is Dredging – History, Importance And Effects
Dredging removes the deposits percolated underwater to clear the water pathway for ships to pass, creates adequate space to construct important bridges, dykes and dams and weeds out silt, intoxicants and pollutants from the bottom of the water.
Once the hoppers are full, the process is halted for a while, and the ship travels to the water disposal site, where the unwanted sediments are released through the bottom of the ship.
What is the Dredging Process?
It involves excavating naturally deposited sediments or artificial debris such as rocks, bottom sediments, construction debris, refuse, and plant or animal matter on the bottom of shallow seawater or freshwater.
The dredge operator lowers it to the side of the body of water or its bottom. The rotating cutter bar uses its sharp blades to loosen the sediment on the bottom, and it is sucked in using a submersible pump. Ultimately, disposal barges or dump scows empty the material at the disposal area.
In general terms, dredging implies digging up the gathered sediments from the seabed and disposing of them at another site.
The oldest known dredging activities are dredging for peat excavation and maintenance dredging. Maintenance Dredging is a broader term that includes clearing deposits and cleaning, widening or deepening a water body using a suction or scooping device (generally called a dredger).
Regular maintenance dredging is of enormous importance in coastal regions with sizeable tidal activity and in water bodies that are susceptible to becoming silted with sediments, sand and mud. The Lowlands of the Netherlands and Flanders are the best examples of regions requiring regular maintenance dredging.
For dredging, dredgers are used to remove the deposited sediments from an inlet creek, waterway or ocean floor.
The process is a blended essence of the following three independent elements: excavation, transportation of excavated material and then usage or proper disposal of dredged material.
When did Dredging Start?
With the beginning of civilization, commodities were transported by inland waterways and oceans. But this transportation depended on the ability of ships, which in turn largely depended on the water depth.
Silting, the natural phenomenon of deposition of silt and sediments over the sea bed, created a constant threat to the voyages of ships.
People started fighting the problem of siltation to ensure the safety of voyages. Still, due to a lack of equipment for removing siltation, they started manually digging the mud by hand, which was inefficient and limited to shallow waterways.
In the 15th century, increased trade at seas necessitated the development of some bed scratchers such as “Zeeuwse Krabbelaar”, a primitive bed leveller. These bed levellers cum scratchers were used to pick the sediments and dispose of them. These dredgers developed from ancient mills to modern suction dredgers.
Mills was developed around 1575. These were a sort of dredging equipment used for digging in ports. Mills had a rotating chain connected with wooden boards, and these wooden boards dug up the mud.
At the primary stage of the development of mills, they were manually driven later. Steam engines powered them. Mills had gone obsolete in 1857 with the development of a suction dredger in the United States.
In 1867, a revolutionary development came with the evolution of the design of a suction dredger by a French engineer. He successfully used this suction dredger in dredging the Suez Canal. From then on, dredging by suction became more and more common.
Then came cutter suction dredgers and trailing suction hopper dredgers in the 19th century. These are modern dredgers and can avail efficient dredging. These were so efficient that they allowed shipping and dredging simultaneously without hindering the traffic.
Recent dredging evolutions have optimised the dredging process as its primary focus rather than developing new dredgers. So, standardizations of dredgers and equipment and advancements in control and monitoring systems improved dredging greatly.
Importance of the Dredging Process
Dredging is an activity of enormous importance in the maritime industry. It serves the following purposes:
- It helps safer voyages by pacifying underwater traffic and maintaining proper bottom clearance.
- Dredging increases the depth of navigation channels, ports and berths, allowing for the free flow of maritime traffic.
- Sometimes, dredging is employed to extract ocean gems such as shellfish and molluscs. So, dredging can help in exploring excellent varieties of these sea creatures.
- Dredging is a primary requirement to channel the construction of a network of bridges, dams, or other civil engineering works in water. These are only proper dredging tools that remove the requisite amount of underwater silt and different compositions and make the excellent constructions accurate that a civil engineer wonders.
- Dredging is also essential to make the marine ecosystem pollution-free. It helps in the eco-friendly disposal of deposited polluting toxicants and harmful materials without causing any harm to the marine ecosystem.
- Dredging helps preserve flora and fauna in water bodies and is also used for recreational activities.
Various Dredging Methods
The dredging process combines digging the soil in the water bed and removing or extracting that soil from the excavated surface by creating a vacuum or plain suction. Technologies assist modern dredges; however, the basic excavation methods of dredges have remained the same since the late 1800s. Depending on how the debris is extracted from the site, there are three main types of dredges.
The common types of dredging methods are-
Mechanical Dredging
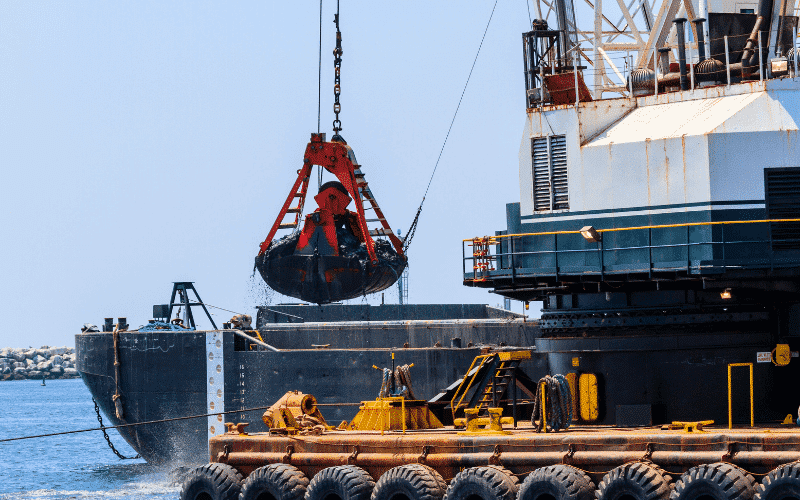
Mechanical dredging is the process in which the sediments are picked up using mechanical tools such as buckets and grabs mounted on a large barge and placed in a waiting barge until the solids settle down. Dipper Dredges and clamshell dredges, named after the scooping buckets they use, are the most common types of mechanical dredges that can work in tightly confined areas.
Mechanical dredging is usually carried out near the shoreline. Hence, mechanical dredging is used to remove sediment on land or shorelines.
The dredged sediment is picked up and placed on nearby land or in water or, most of the time, in another barge dedicated to carrying the sediment. If the dredging is done near the shoreline, the sediment can be directly transferred to a truck or railway wagon.
The mechanical dredging operation can be done using a barge or operated from shore.
If the mechanical dredger is onshore, it has a limitation of covering the area as it can only be used near the shoreline. Barge-type mechanical dredgers can be operated in any water; however, it will be most effective near docks, piers, etc.
Mechanical dredging can be a continuous process. However, the quantity of the sediment will be limited to one scoop, which is lifted every time to remove the residue. The mechanical type can dredge hard compacted sediments, and water carryover is way less than hydraulic dredging.
Hydraulic Dredging
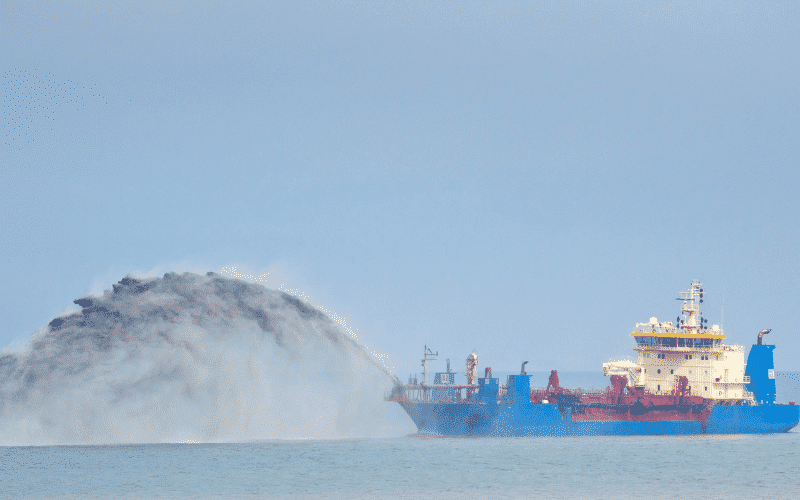
In the hydraulic dredging process, centrifugal pumps remove the sediment from the dredged site. Material from the channel bottom is sucked into the pipe.
The sediment is mixed with water and made into a slurry mixture, making it easier for the pump to transfer. Depending on the pumping distance, a booster pump can be fitted inline to transfer the sediment to the nearest shore through larger ships to maintain a constant production rate.
One of the significant advantages of the hydraulic dredging process is the elimination of other transport mediums or equipment, as the sediments can be directly transported to the shore facility, saving additional expenditure and time.
The advantages of hydraulic dredging are:
- Reduces capital costs
- Reduces use of equipment and transportation
- Reduces energy and emissions compared to the mechanical dredging process
- Safe and efficient
- Hydrodynamic Dredging
Hydrodynamic dredging is generally used to maintain the channel, port, harbour depths, etc. If a new site needs to be freshly dredged, this method won’t prove valuable and efficient. Once the area is dredged, it must be constantly maintained to avoid unsafe navigation by retaining the required depths.
Related Read: Mastering Ship’s Navigation
This method utilizes water injection technology, which injects large amounts of water using nozzles attached to a horizontal jet bar powered by pressurized pumps. As the water spray from the nozzle hits the water bed, it fluidizes the sediments, making them loose. This loose sediment near the channel bed flows down to the deeper areas due to natural current.
As the natural flow helps sediment transport, this method is cost-effective and much more environmentally friendly than the other two.
Different types of dredging ships
As per the classification of the dredger, they can be further classified into different types:
Types of Mechanical Dredgers
These are fixed in place using anchor piling, known as spuds.
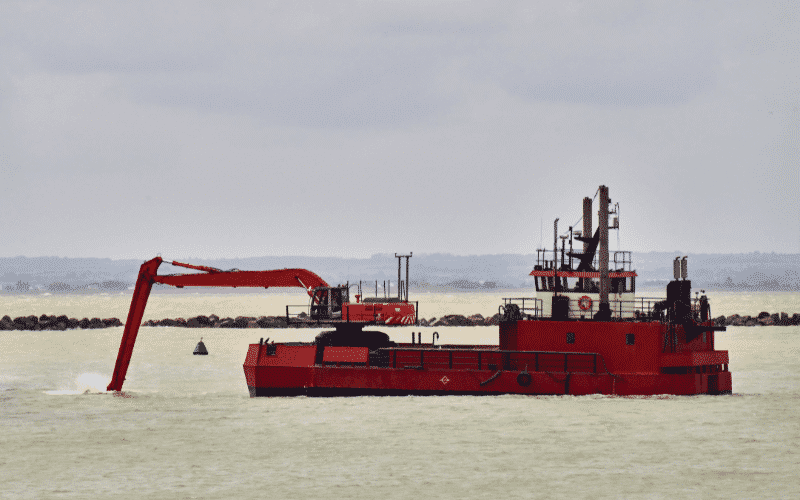
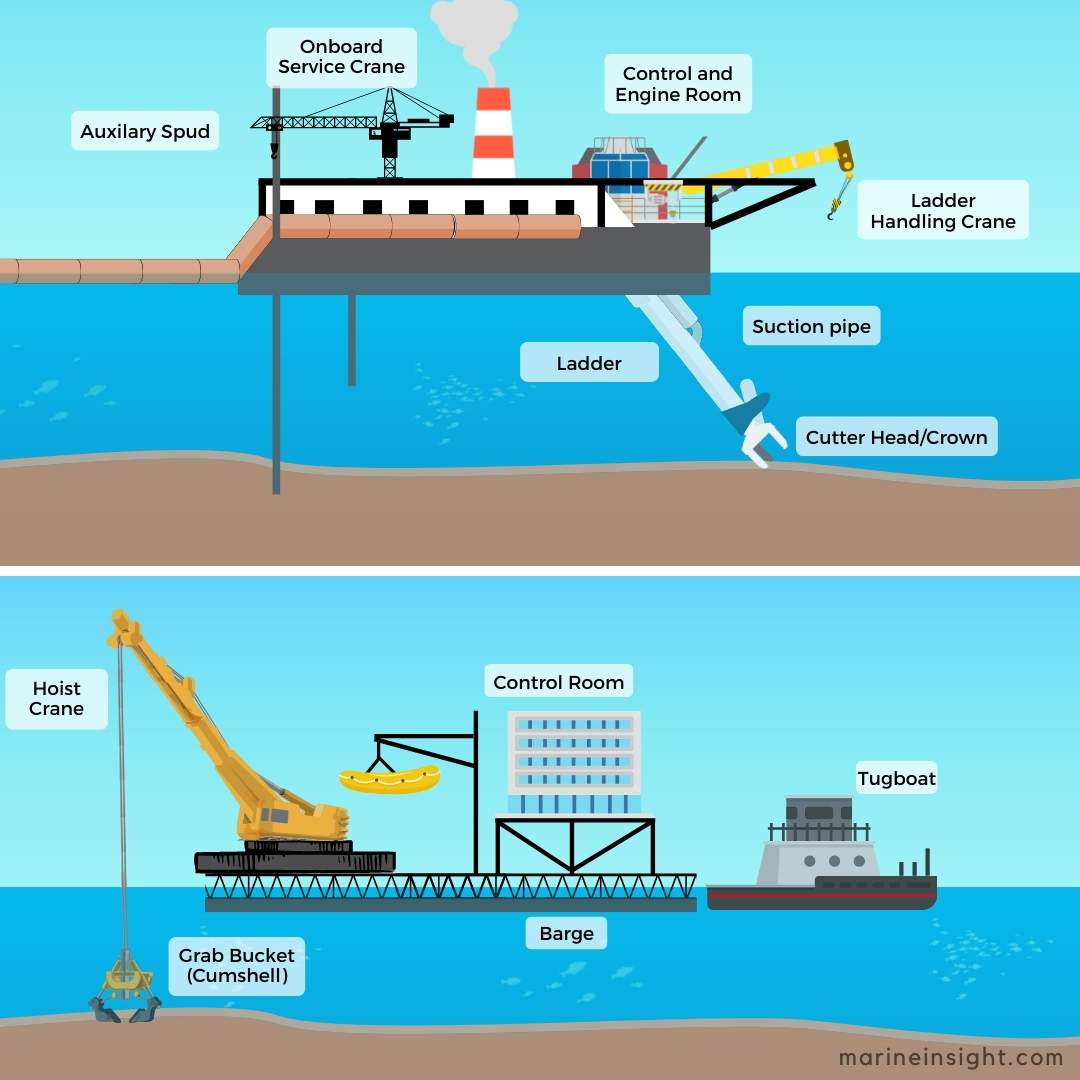
Bucket Dredger: The bucket dredger is usually a fixed-type stationary dredger that rotates in an arc by winches around the dredging site. The scrapping end is fitted with a bucket, which removes the sediment or bottom material, and when turned upside down, the sediments are unloaded on a barge.
Grab Type Dredger: This is a stationary dredger with a grab as a dredging tool (Two equivalent scoops or shells operated hydraulically). Due to its design, It is also known as a clamshell dredger. There can be different designs of the grab, which can be used for deepwater dressing.
Backhoe Dredger: Also known as fixed arm dredger, it is a stationary type dredger usually mounted on a barge or works near the banks. The dredging equipment is a half-open shell with a fixed-length hydraulic arm used in shallow waters and near harbour sites.
The main types of Hydraulic Dredges include
Suction Dredger: It is a stationary dredger generally used for mining sand. It is also the best equipment for removing sludge from wastewater treatment plants or where heavy-duty sediment removal is required. The suction pipe of this dredger is inserted into the sand deposit, and water jets are used to bring the sand up from the excavation site. The sediment can be pumped by sucking the sediments into the pipeline and transferring it to the reclamation site or loaded into barges, depending upon the location and available transfer arrangement.
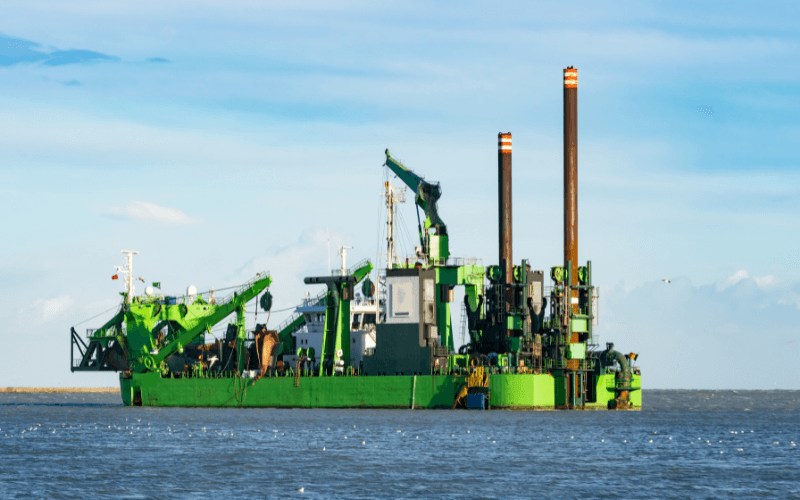
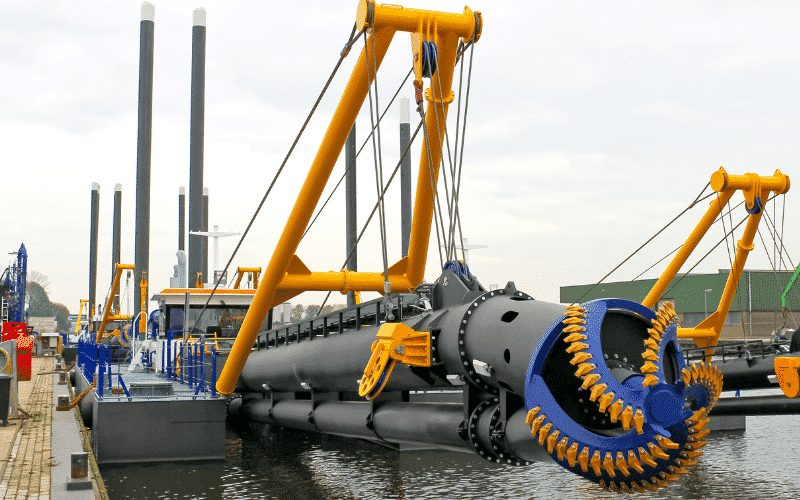
Cutterhead Suction Dredger: It is another stationary dredger with a cutter head on the suction end to loosen the base to be dredged. Like the plain-suction dredge, the sediments are sucked and pumped via a discharge pipeline ashore or into barges. The cutter head can be of different designs and materials, depending upon the properties of the surface to be dredged. It aids in removing sediment from hard surfaces.
Auger suction dredge operates on the same principles as a cutter-suction dredge, except that the mechanical cutting tool is a rotating Archimedean screw placed at right angles to the suction pipe.
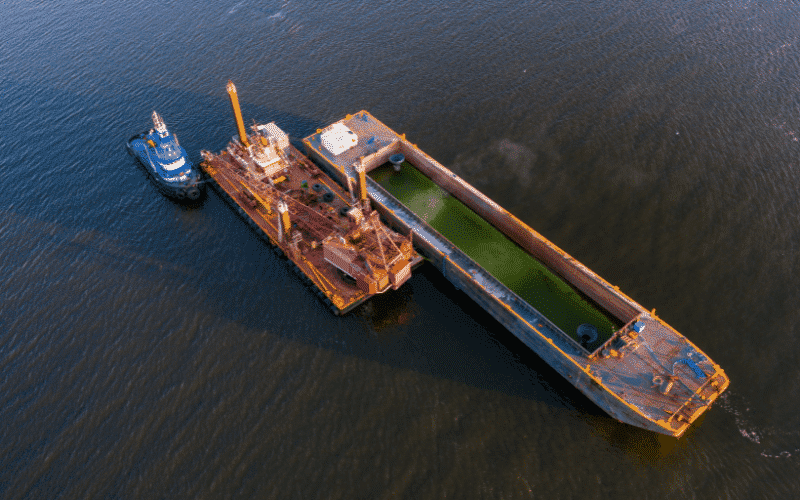
Trailing Suction Hopper Dredger: This is a self-propelled ship carrying the dredger equipment having a hold or hopper arrangement to fill it with excavated material while following a pre-set dredging operation. This type of dredger can open the bottom of the hold to unload the dredged material into the designated site. This dredger is mainly used in open water such as canals, rivers, estuaries, etc.
Reclamation Dredger: This assists equipment in the dredging operation, not the dredger itself. It is used to empty the hopper barge sediments using a suction pipe, which can be lowered into the hopper barge hold. Additional water can be sprayed to make the sediment slurry for easier suction and transfer to the dedicated site or shore depot.
As explained earlier, hydrodynamic dredgers have only one type: Water Injection dredgers.
Few other types of dredger ships
Amphibious dredgers: These ships have the unique constructional feature of working out of the water surface using long legs as their base. They can be equipped with grabs, buckets or a shovel installation.
Air-lift dredgers: This dredger uses high-pressure air jets instead of water jets for material flow at the mouth of the suction pipe.
Bed leveller: This type is used to level the bed surface, which has recently been dredged. It consists of a long flat blade or heavy bar connected to a tugboat at the end, and when it is pulled, it will level the surface on the dredged surface over short distances.
A hopper dredge is a ship that sucks up the sediment slurry and holds that slurry in the ship (hopper) until it gets to its destination. A pipeline dredge sucks up the sediment slurry and pumps it through a pipeline directly to its destination.
Related Read: Different Types of Dredgers Used in the Maritime Industry
Effects of Dredging
But like every coin has two sides, even dredging, despite all the positive attributes to the process, has negative points. These negative points are also important because they tend to impact the existence and life of the marine habitat.
These adverse effects of dredging are briefed as follows:
- When dredging is carried out for marine engineering or construction work, a large amount of water must be removed and stored at another location. This creates a minor storage problem but extensively affects the life of flora and fauna prevalent in that water. This is due to a change in the mineral composition of water before and after dredging and depositing it back in its source after construction.
- Dredging impacts the crops badly in the regions where it is carried out to de-silt the rivers, primarily intended to quench the irrigation demand of the area. Along with silt, essential minerals also get dredged out, leaving the resultant water and land lacking in nitrates and phosphates.
- Also, if dredging is carried out to serve the cleaning purpose, removing the toxic waste alarms the safe disposal problem. If it is disposed of on land to make the ground barren and in other less critical water bodies, it harms the living creatures in that water body.
Related Read: Effects of Dredging on the Marine Environment
These ill effects of dredging become insignificant compared to applications and the importance of dredging but should be kept in mind and catered to where necessary.
Conclusion
The dredging industry has developed throughout the world in the last two decades. It serves multi-purposes such as cleaning, maintenance, disposal, transportation, excavation, etc., at a time. It helps make the water navigable and makes fishing easier, even in shallow creeks. It helps remove contaminants from the waterways and recreate damaged areas through reclamation works.
But a vital thing we must cater to while dredging is the safe dumping of managed. It should be disposed of where no significant landform or life-form get harmed. Also, in some areas, dredging alters the mineral composition of the water; precautions should be taken to oversee the alterations caused by the change in mineral composition.
By putting small things in place, we can prevent the occurrence of a significant catastrophe. Today, with the advancement in dredging technology, we have pushed dredging towards higher efficiency with lower environmental impact.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is dredging bad?
Dredging is harmful to marine flora and fauna. It impacts them negatively in many ways through habitat destruction, entrainment, noise pollution, sedimentation, and contamination.
2. Why should you dredge a pond?
Maintaining perfect water quality is essential for a healthy pond. Dredging a pond aids in the proliferation of good bacteria that aid in breaking down the organic waste that collects at the bottom of the pond.
3. There are how many types of dredging methods?
There are three kinds of dredging methods: mechanical dredging, hydraulic dredging and airlift dredging. Dredging is usually performed using equipment called dredges that are held on a barge.
4. How does a dredge work?
Dredges are unique equipment that loosens the bottom sediment and creates a vacuum to suck and pump out the unwanted sediment and debris, which is then transferred to a disposal site.
5. How does dredging affect the water quality?
Dredging impacts the water quality of marine systems manifold. It depends on the nature of the dredged material, as the seabed disturbance changes the chemical composition or the ph of the water body, ultimately impacting the whole marine ecosystem. For instance, excessive sand dredging degrades rivers and estuaries.
Disclaimer: The author’s views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of Marine Insight. Data and charts, if used in the article, have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and Marine Insight do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendations on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and Marine Insight.

About Author
Raunek Kantharia is a marine engineer turned maritime writer and entrepreneur. After a brief stint at the sea, he founded Marine Insight in 2010. Apart from managing Marine Insight, he also writes for a number of maritime magazines and websites.
Latest Shipboard Guidelines Articles You Would Like:
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Subscribe To Our Newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.
Web Stories























Is there any dangers about dredging in the world. I would like to know. thank you
i work on drege,lake was old gravel pit, worked about 7yrs. til business moved to far to another lake.it a 2 zpud dredge w cutter an about 1000 ft of poly pipe attached to barrels to float. which gave material to a sand plant .really like that job
Thank you for sharing your experience John ??