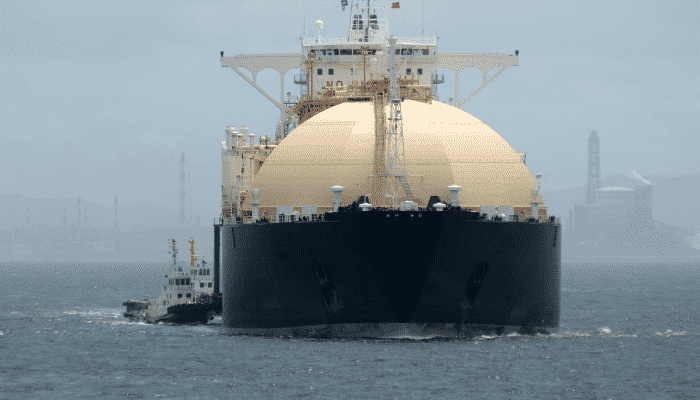
LNG Tankers – Different Types And Dangers Involved
A tanker ship with temperature-controlled tanks which are intended to transport Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG), is termed as LNG tanker or LNG Ship.
On an estimate, about 360 LNG tankers have been developed (advanced and specialized) for the transportation of LNG, round the globe till date.
These vessels, unlike other tankers, have a propulsion system which is fueled with natural gas, thus, emitting lesser greenhouse gases.
These tankers should be capable of bearing high pressure and the temperature inside these tankers should be maintained at about -163˚C.
As the LNG gas is to be transported in its liquid form, it must be transported in vessels having the high-pressure bearing capacity and lower inner temperature.
As per the requirement of LNG ships, these can be of three types namely:
- fully pressurized;
- semi-pressurized and refrigerated;
- and fully refrigerated.
The world’s first LNG carrier was Methane Princess (Methane Pioneer) with a deadweight of 5,034 DWT.
Methane pioneer started its voyage on January 25, 1959, from the Calcasieu River on the Louisiana Gulf Coast to the United Kingdom. It carried the world’s first ocean cargo of LNG and delivered it safely to the UK.
Related Read: Top 5 Zero-Emission Ship Concepts Of The Shipping World
Classification Of LNG Carriers
LNG vessels can be classified into four categories in terms of cargo containment systems:
Moss( Spherical-Type B)
This system is named after the company which designed them i.e.; The Norwegian Company Moss Maritime. Most of these types of vessels have 4-5 tanks. These tanks here have a working pressure of 22 kPa(3.2 Psi) which can be increased in case needed.
Related Read: World’s Largest MOSS-Type LNG Transport Vessel ‘PACIFIC BREEZE’
IHI(Prismatic-Type B)
The self-supporting prismatic type B tank is designed by Ishikawajima-Harima Heavy Industries which are employed in only 2 vessels. They cater to the problem of “sloshing “over the membrane LNG carrier tanks. Because of the several incidents in the past, these tanks were constructed to sustain internal accident damage due to internal equipment releases.

Related Read: Different Types of Tankers: Extensive Classification of Tanker Ships
TGZ MARK III
These are the membrane type design which is designed by Technigaz. This consists of waffles, the primary barrier is made up of stainless steel of 12mm thickness and the secondary membrane followed by a primary insulation which is anew with secondary insulation. All these barriers are supported by the ship’s structure from outside.
GT96
This design designed by Gaztransport consists of primary and secondary membranes made up of a material Invar which has no thermal contraction. Here the plywood boxes filled with perlite is used for insulation which is flushed with nitrogen gas.
CS1
The combined system no.1 was designed by Gaztransport & Technigaz. In this design, the best 2 components namely Mkll and No96 systems are used. Here primary barrier is constructed up of Invar and secondary from Triplex. Till now only 3 vessels are made using this membrane system by 1 shipyard.
How Much Does An LNG Tanker Hold?
Double-hulled construction is used to build LNG Ships. Each ship consists of four or five large tanks to retain liquefied gas. These cargo containments can either be spherical (Moss sphere design) or geometric membrane (membrane design) and each containment are made in multi-layers. These layers of tanks make them leak-proof and help in maintaining the necessary colder temperature inside. These tankers are also equipped with fire alarms and proper insulation system.
Before 2006, the carrying capacity of LNG carriers was typically in the range 80-135,000 cubic meters. But with the advancement in technology, in 2006, the first LNG ship of capacity over 200 and 266,000 cubic meters were being constructed in Qatar.
In the beginning, the shipping of LNG was quite uneconomical. This was due to the smaller size of the LNG shipping container and higher voyage and other expenses. But with the advancement in technology and development of bigger size LNG vessels, the shipment of liquefied natural gas became more economical, safer and more efficient.
Related Read: Properties Of Membrane Tanks For Transportation Of LNG Cargo On Ships
Largest LNG Tanker In The World
The first known tanker was very small of only 5034 DWT, but with the development of technology in developed countries around the globe, there was a revolutionary advancement in size of LNG carriers. That is why today we have an LNG carrier with 128900 DWT.
MOZAH vessel of Qatar, developed in 2006-2007 and launched in 2008, is the world’s largest LNG carrier today. It has a capacity of 266,000 cubic meters and a size equivalent to about four football grounds (345m length and 53.8m width). In a special ceremony organized at Samsung Heavy Industries shipyard on Geoje Island, her Highness Sheikha Mozah Bint Nasser Al-Missned named the first largest Q-Max LNG Carrier, “MOZAH”. The vessel is used to carry LNG produced by Qatargas II (also Qatar Liquefied Gas Company Limited) to Europe. MOZAH sails under the flag of Marshall Islands.
Hudong-Zhonghua, a shipbuilding company of a Chinese state with the collaboration of Norway based society revealed an underdevelopment project, which is likely to be completed by the next year. They have promised to build, through this project, an LNG ship with a capacity of 270,000 cubic meters. If completed it will become the world’s largest LNG carrier.
Specifications of MOZAH:
- MOZAH, an LNG carrier of Q-Max has a length of about 1,132 feet or 345 meters, along with a 53 m (174 feet) beam and a 12 m (39.4 feet) summer draft. This giant size of the carrier and its high capacity make its voyage profitable and efficient.
- The gross tonnage and effective deadweight tonnage of MOZAH vessel scale to 163,922 GT and 128,900 DWT respectively. The high values of DWT and GT allow the cargo ship to carry 266,000 cubic meters (9,400,000 cubic feet) of liquefied natural gas at an approximate temperature of −163 °C (−261 °F).
- The engine used to drive Mozah is 2 MAN B&W 7S70ME-C two-stroke low-speed diesel engine which is electronically controlled. The total output power of the engine values to 43,540 kW (58,390 horsepower) @ 91 rpm.
Related Read: Understanding The Design of Liquefied Gas Carriers
Dangers In LNG Ships
Major exports of LNG is carried out on the west coasts, which introduce thousands of LNG tankers per year. Most of these tankers pass through narrow waterways and densely populated areas. So, the dangers in LNG ships should be taken seriously.
LNG is actually, odourless, colourless and non-toxic, chilled methane gas at -162 °C, which is actually inflammable but when it comes in contact of air it rapidly converts into vapours which catch fire easily.
This fire can grow up to 150 m high and burns for a long time. Major dangers in LNG Ships are- Explosion, Fumigation, Spills, etc.
Some major dangers of LNG ships are briefed as under:
1. Explosion
Most severe risk generating danger of LNG ships is the explosion of LNG ships. The flames of LNG are very high and have greater lateral reach. The explosion not only damages the reputation of the ship but also causes non-recoverable loss i.e. the loss of lives of the crew of the vessel.
Major areas of risk: The three main areas of LNG ship are highly prone to the risk of explosion are – the engine room, motor rooms and cargo compressor rooms. These areas must be provided with CO2 fire suppression systems. The fire systems should meet the requirements of ISO 14520 and also comply with PFEER codes.
Prevention: All the types of equipment used to form the LNG carrier should be intrinsically safe and approved from the standards, thus ensuring the protection of crew against the danger of explosion.
Personnel and equipment inspecting the vessel should be properly guided and provided with fire suppression systems. Yet LNG is inflammable but it is dangerous when coming in contact with an ignition source. As per the records of IMRRA (International Maritime Risk Rating Agency), from the total LNG carriers, 12.5% of the carriers were placed in the explosion risk category in 2017.
Today, Smart ultrasonic technology is used in the fire suppression system and ensures more safety.
Case Studies: The past years witnessed many serious cases of tanker fires. A Chinese Tanker exploded in March 2017, which resulted into serious damage to the vessel and 3 crew members also went missing. In 2012 an explosion was witnessed in central China resulting in loss of lives of 5 crew members.
Related Read: 12 Types of Maritime Accidents
2. Risk of vapour cloud explosion
LNG vaporizes very soon, so the volume of gaseous LNG becomes 625 times the earlier volume of liquid LNG. As soon as the LNG tank of LNG ship leaks, with the leakage of liquefied natural gas in air, its initial flash vaporization starts and generates a lot of steam instantaneously.
When this steam mixes with its surrounding air it forms cold steam fog and white smoke after condensation in the air. It then gets diluted and heated to form a flammable gas cloud with air and reaches explosive concentrations (5% 15%), which will lead to a vapour cloud explosion. This vapour cloud explosion changes into boiling liquid explosion and finally break out as fire risk.
Fire Risk: LNG is highly explosive and flammable when comes in contact with the atmosphere with the ignition point of 650. Its flames propagate rapidly and burn a large mass approximately doubles to that of gasoline or other oils. It has a property of recrudescence, re-explosion and it is difficult to stamp it out.
As the LNG in the tanker is stored at a lower temperature, excessive thermal stresses are produced due to local cooling, which results in loss of ductility of hull structure and produces brittle fractures in hull structure.
Related Read: What is Rollover Condition in Gas Carrier Ships?
3. LNG Spills:
When LNG spills over the water it causes cryogenic burns, asphyxiation, dispersion, fires, and explosions. These all are the matter of major concern in regard to public safety. Necessary safety measures should be taken to make the voyage safer.
LNG spills were not considered dangerous until a ship having spill collides with another ship and results into explosion because without a source of ignition spilt LNG is not harmful as it vaporizes from water rapidly, causing no damage to the environment as well as to the aquatic lives.
Approaches to reduce consequences of LNG spills: Potential dangers from an LNG spill in waterways can be reduced with the help of certain modern techniques or a combination of approaches, by using improved safety equipment in LNG tankers, by proper supervision and improving security of ship, and by taking precautions in various operations to prevent or lessen a spill.
Explosions (that generally take place in confined spaces), combustion events and their rapid phase transition can potentially lead to the secondary damage of spillage of LNG.
Following are the approaches to manage the consequences of LNG Spills:
- Security and safety systems of both ship and terminal, which include improvement in surveillance or supervision, up-gradation of insulation of tanker and other standoff protection systems of the tanker. Tugs, ship crews, and vessels should be provided with improved surveillance.
- By improving and modifying LNG tanker escorts, extending control zones of the vessel and by improving safety operations near ports and terminals. Proper checking should be availed of offshore mooring and offloading systems.
- Proper functioning of emergency response systems for reducing fire and dispersion hazards should be facilitated. There should be proper emergency response coordination and it should allow proper communication with rest oh parts of the ship.
- Keep the ship into a safe zone, i.e. in an area which is more than a mile away. It results in a safe voyage, but certain provisions should be followed if the distance is to be reduced to half a mile to a mile, If the distance between obstacles, which may be another ship or any natural obstacle, and the ship is less than half mile the spill may burn off the ship, and therefore voyage should be avoided in that case.
These risk-reducing techniques are helpful in major risk-prone zones where the damage to life and property is maximum and which can’t be replenished. If the explosion of liquefied gases can be controlled then the spillage causes a little or no damage to the marine environment as most of the liquefied gases are the non-polluting, clean and non-toxic product.
The only thing to be catered during the liquefied gas spill is that it may create large quantities of vapour when diluted with seawater, and these vapours may cause a fire break out or explosion or certain health hazards.
Related Read: How Does LNG Terminal Works?
4.Fumigation:
It is the process of mixing of liquefied natural gas from the engine room or other congested parts of the ship with the charged air so as to cause suffocation and make the environment poisonous. It is more commonly an outcome of LNG spills. To reduce fumigation of LNG tankers the following types of equipment provided should be in proper working condition:
- Manual shut out valve
- Filter
- Vapour draw regulator
- Dual shutoff solenoid valve
- Electronic Throttle Body
Also, proper ventilation and exhaust valves can reduce the effect of fumigation by releasing the fumigants to the external environment. The risk of fumigation of LNG tankers is also less because the LNG containments are made up of 8-layered insulating material.
Since the 1960s, liquefied natural gas shipping industry ships bulk quantity of liquefied gas in containers. There have been recorded more than 33000 voyages since 1964 covering almost all the seven continents. There are certain dangers in shipping LNG through marine vessels which mainly include: LNG Spills, Explosion and Fumigation. Out of these, all explosion is most dangerous due to which LNG Ships are regarded as floating bombs because sometimes explosion caused by them is more severe than the explosion of some atomic bombs.
Related Read:
But LNG can be shipped properly if preventive measures are taken. Hazards caused by other liquid fuels such as gasoline, diesel etc are much more as compared to LNG. Liquefied natural gas causes no damage to aquatic life because it vaporizes (if no source of ignition is present) as soon as the LNG is spilt over water.
The LNG shipping industry has impeccable safety records. LNG is considered extremely well amongst any of the large transportation and shipping materials.
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of Marine Insight. Data and charts, if used, in the article have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and Marine Insight do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendation on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and Marine Insight.
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Latest Type Of Ships Articles You Would Like:
Subscribe To Our Newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.















I am interested to buy Expired Vessel. please let me links where I see to buy.
MY JALNIDHI STEAMSHIP COMPANY LTD IS INTERESTED TO BUY LNG TANKER SHIP IF VEDANTA -CAIRN NEEDS LNG TANKER SHIP
ANILKUMAR D BHATT
CHAIRMAN &M.D.