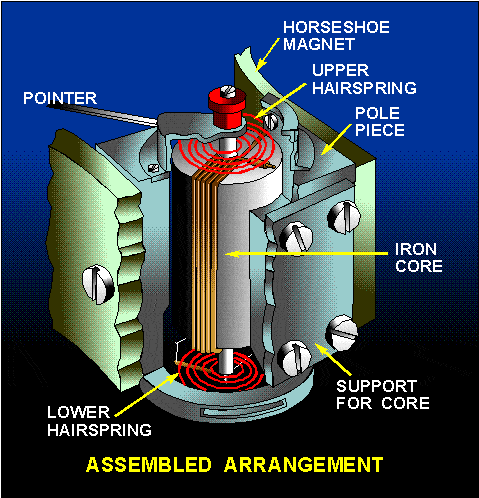
Featured News
Latest Articles
What is a Continuous Discharge Certificate or CDC?
Watch: Giant Disney Cruise Ship Maneuvers Through Impossibly Narrow River
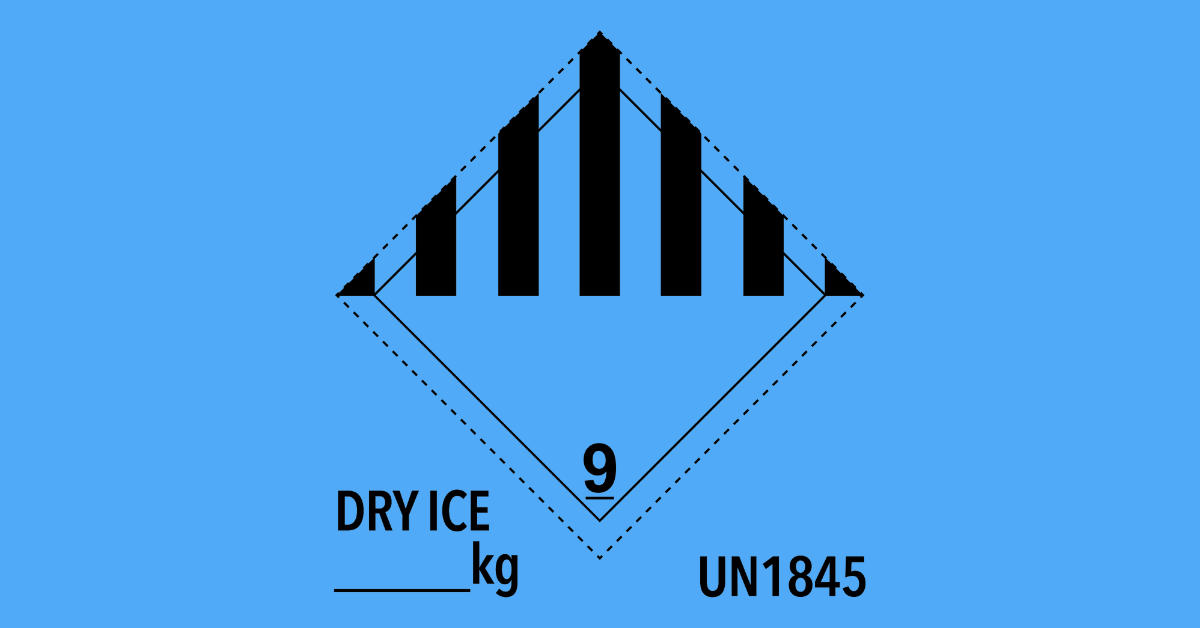
Why Dry Ice Is Used For Packaging
Real Life Incidents: Near Miss In Open Water And Good Visibility
Real Life Incident: Poor Situational Awareness Leads to Collision
Real Life Incident: Monkey’s Fist Knocks on Office Window
Maritime Law & Logistics
Minimum Quantity Commitment (MQC) and Liquidated Damages in Container Shipping: Concept and Relevance
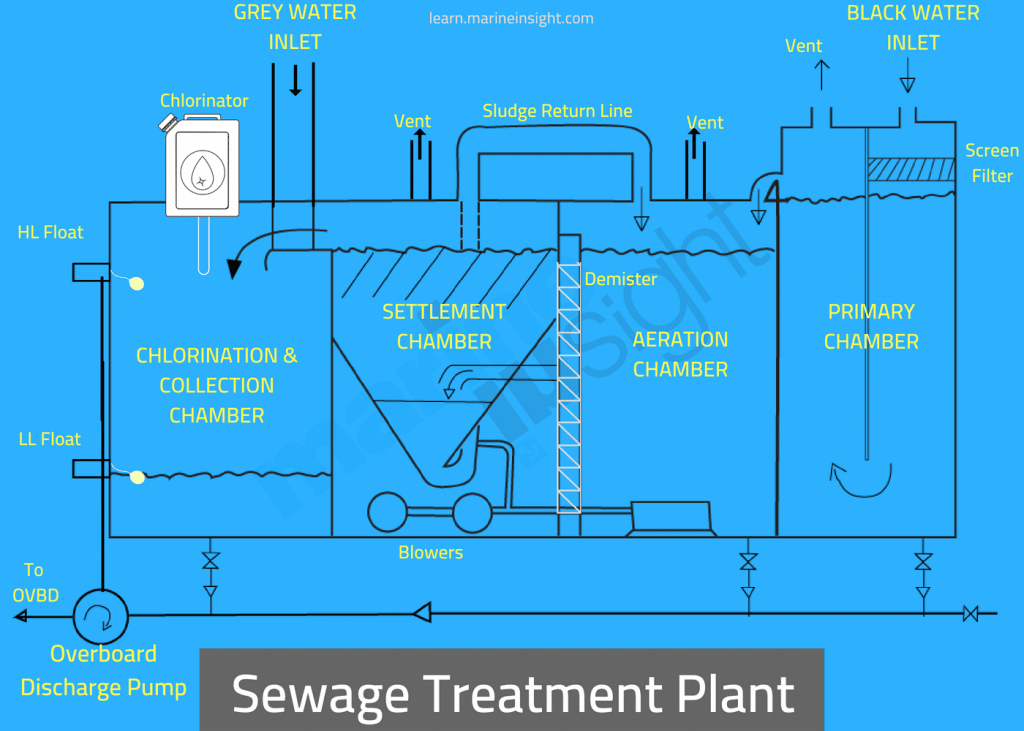
MARPOL (The International Convention for Prevention of Marine Pollution For Ships): The Ultimate Guide
Read More From This Category >