Who Are Clearing Agents – Importance And Duties
Developing economies, bilateral and multilateral trade agreements between countries, and improved and advanced information systems and logistics infrastructure have resulted in burgeoning global trade.
Lead times in the procurement of goods have reduced drastically, thanks to these advancements. Statistics released by the World Trade Organization (WTO) for the year 2019 shows that globally USD 19 trillion worth of goods were exported during the year. This converts roughly to the same amount in imports that were handled by clearing agents!
Consumption decreased this year as a result of the coronavirus pandemic and industries scaled back their production to adjust to the dip in demand. However, the good news is that global trade and the movement of goods are showing promising signs of picking up again.
An increasing number of businesses have used this opportunity to their advantage by adapting to the situation to carry on with their businesses.
The current trend of outsourcing has encouraged the activities of clearing and forwarding agents. You may still find business houses handling their own cargo clearance and freight forwarding but the role played by clearing agents especially in the clearance of cargo has grown manifold in the last few decades.
By having a responsible third-party to handle the company’s clearing and forwarding activities, business organizations are able to focus more on their core business.
Though it is common to find agents, usually known as C&F agents (clearing & forwarding agents) handling both functions on behalf of their customers, strictly speaking, these functions of clearing and freight forwarding are different activities.
While a freight forwarder can be seen as an entity who undertakes to transfer cargo of the customer from one point to another, the clearing agent is an agent who completes all port and customs formalities on behalf of the consignee or receiver of cargo at the destination port.
In this article, we will take a look at the duties and importance of clearing agents especially in relation to trade and freight by sea.

Who can be a Clearing Agent?
Clearing agents are also called customs brokers or customs house agents. To operate as a valid clearing agent and clear goods, most countries require a clearing license issued by the relevant authority.
In the US, clearing agents are licensed by the US Customs and Border Protection (CBP) after they pass the exam conducted by the CBP. The UK is an exception and any valid business can operate their own customs broker.
In India clearing agents require a license to operate. They have to prove their financial standing and pass a written exam followed by a viva voce (oral exam). However, import/export houses in India can operate on their own at specific customs points where their goods are required to pass.
Clearing agents are normally registered with the local port and customs authorities, overland customs points, or any other government agency within their area of operation.
Just as in other trades, most countries have their own set of regulatory requirements for clearing agents.
Duties and Responsibilities of a Clearing Agent
It is clear from the above facts that the job of a clearing agent involves very specialised tasks and they are regulated by the country’s government.
Clearance of cargo from the seaport or a country’s border crossing is a complicated process that requires good operational and organizational skills. Apart from these skillsets, they must have a good knowledge of the local laws and customs formalities.
Clearing agents should also be familiar with the software that is used for the entry of shipment data and any other details that are required to be input into the relevant government information systems portals.
Goods that are waiting to be cleared may first have to pass inspection by customs authorities. Operational and organisational skills of clearing agents come into play for the arrangement of such inspections by authorities.
Labour and equipment such as forklifts and pallet jacks have to be available at the right time. Timely and prompt inspections facilitate quick transfer of the cleared goods to the customer’s storage facility.
Clearing agents may be required to arrange labour for loading and off-loading. The right labour force that can use special loading/unloading equipment will have to be made available at the correct time of loading and off-loading as it might also involve customs personnel as observers during these activities.
All activities related to the clearance and transport of cargo will have to be monitored, dues paid, and the consignee kept informed. Subsequently, clearing agents may also be required to submit data and written reports to their supervisors or directly to the consignee regarding clearance and delivery of the cargo.
An important task performed by clearing agents is to prepare and submit the required customs documentation with the authorities for clearance of shipments.
Most countries have switched over to electronic data interchange (EDI) systems into which the required data is entered by the clearing agent.
It is therefore essential that the clearing agent is tech-savvy and can operate the different types of software that are used in his office as well as by the customs.
Depending on the type of goods that is imported, the clearing agent may also be required to inform and submit documentation to regulatory bodies like the Health Department, the Environment and Pollution Control Board, etc.
Food items, alcoholic drinks and tobacco, and chemicals are some examples of such goods.
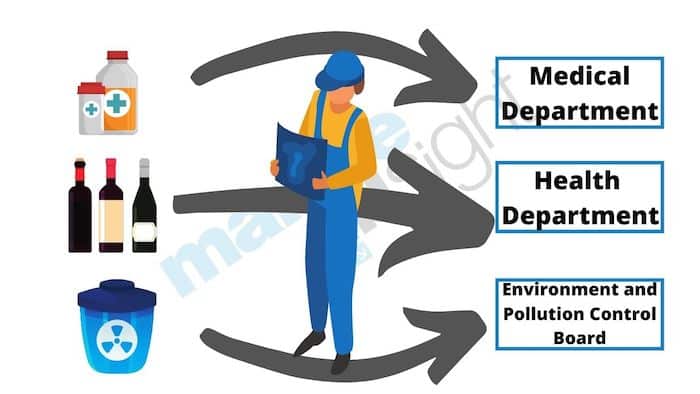
Such items are usually subject to inspection by officers from these regulatory bodies before they give their approval to import them into the country. Those goods that do not meet the conditions as laid down by the country’s laws may have to be returned.
Sometimes the problem could be with documentation of these items. It may be possible to make certain modifications to the original documentation that would make it possible to import such goods into the country.
Certain goods that are banned in a country may have been traded inadvertently between the seller and buyer. Banned goods can only be returned to the exporter failing which it will have to be destroyed under the supervision of the relevant authority. Such items could include alcoholic drinks, certain types of drugs, etc.
Clearing agents will be required to liaise and coordinate with the relevant authority for the destruction of such goods. They will have to work closely with the consignee, the concerned regulatory body or bodies, and sometimes the carrier to complete this task and a certificate of destruction is issued by the authority.
Some goods may have serious labelling errors on them. These could be errors in the label format or certain details could be missing.
Some of the information that is shown on product labels is the name of the product, its ingredients (if applicable), date of manufacture, date of expiry, country of origin, statutory warnings, etc. In the case of a labelling error, the required modifications may be allowed by the concerned regulatory body after which the import procedures can be completed.
One big advantage in using dedicated clearing agents to clear cargo shipments is that they can do it easily as they usually have a good rapport with port and customs authorities as well as with transport and labour unions.
Documents Required for Clearance of Goods
What are the documents that a clearing agent will need, to affect the smooth clearance of goods from the port through customs? Which are the documents prepared by the clearing agent? Let us look at some of the important documents that are handled by the clearing agent.
- Bill of Entry
- Bill of Lading
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing list of goods
- Certificate of Origin
- Import license of the consignee
- Insurance certificate
- Letter of Credit (L/C)
Bill of Entry
The bill of entry is usually prepared by the clearing agent and submitted to the customs authority before the arrival of goods at the destination port.
The agent has to ensure that the correct description and value of goods are shown on the bill of entry and that goods come under the correct HS Classification (Harmonized Systems code). The HS Classification system is an internationally accepted system of classification and coding of goods. The customs duty calculation will be based on the HS code.
Most of the ports these days have the facility to prepare bills of entry digitally. The clearing agents only have to input the correct data through the relevant customs portal.
Bill of Lading
A signed bill of lading is issued by the ocean carrier as proof of receipt of cargo from the shipper, onboard the ship. It also gives title over the cargo, normally to the consignee. It shows the name and address of the consignor, consignee, and notify party (if applicable). The clearing agent has to ensure that the bill of lading accompanies other documents for clearance of the cargo.
Commercial Invoice
Another document that must be submitted by the clearing agent for the clearance of goods is the commercial invoice. A commercial invoice is issued by the seller or consignor and must accompany the goods. It gives the full name and address of the seller and the buyer. It will have the details of the goods that are being shipped, the quantity shipped of each item, their respective costs, and the total amount due from the customer.
Packing List
At a glance, a packing list may look very similar to the commercial invoice. But the similarity ends there. Its heading will show ‘packing list’, and it will have the complete details of the products – most importantly the serial number, description of units, pack and packaging, individual and overall dimensions of each package (if applicable), the weight of each unit and the total weight, and HS code.
The packing list gives a complete picture of what is contained in the shipment, their packing, and weight. All the parties involved in the carriage and clearance of the consignment such as the carrier, the freight forwarder, the clearing agent, port and customs authorities and the customer require the packing list.
It helps them make appropriate arrangements for handling the goods from loading and carriage through to unloading, transport, and stacking in the receiver’s storage space.
Certificate of Origin
A certificate of origin is usually issued by the Chamber of Commerce (CoC) of the country from where the product originates. It shows the country where the product or commodity is manufactured or produced. In some countries, certain other government bodies also issue this certificate to its exporters. In India, for example, the certificate of origin is issued by two government bodies which are the Chamber of Commerce and the Trade Promotion Council of India.
Import License of Consignee
The import license is the permission given to the consignee by the relevant government authority to import the specified goods into the country. This license must be submitted by the clearing agent to the customs, along with other documents, prior to clearance.
Insurance Certificate
Goods are insured against unforeseen calamities and accidents that can happen during transit of the cargo. The insurance certificate shows the type of insurance and the amount for which the goods are covered. The terms of business between the seller and the buyer may be CIF (Cost Insurance Freight) or CFR (Cost Freight). In CIF, the insurance is borne by the seller or consignor whereas in CFR goods are insured by the buyer or consignee.
Letter of Credit or LC
When trading is done through a letter of credit, the bill of lading may show the name of the beneficiary as well as the clearing agent under the notify party field. In such cases, the clearing agent also has the responsibility to follow up with the bank on the release of clearance documents.
Top Clearing Agencies of the World
Some companies have remained on top in cargo clearance through their consistent and reliable performance. The top five, according to trends of the last few years are:
• Kuehne + Nagel
• DHL Supply Chain & Global Forwarding
• Sinotrans
• DB Schenker
• DSV Panalpina (DSV acquired Panalpina in early 2019)
Clearing agents play a crucial role in the import and clearance of cargo. Timely documentation, submission of the appropriate paperwork to authorities, and related subsidiary activities such as arranging the specialised labour and transport, etc. help clear goods quickly and save on money and time.
A slipshod or tardy approach by the clearing agent can mean an inordinate delay in the clearance of goods.
You might also like to read:
- Who is a Shipping Agent?
- What Is CBM Rate In Shipping?
- 50 Marine Careers Essential Guide
- A List of Unique and Interesting Marine Careers
- A Guide To Verified Gross Mass (VGM) For Shipping
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of Marine Insight. Data and charts, if used, in the article have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and Marine Insight do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendation on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and Marine Insight.
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction

About Author
Hari Menon is a Freelance writer with close to 20 years of professional experience in Logistics, Warehousing, Supply chain, and Contracts administration. An avid fitness freak, and bibliophile, he loves travelling too.
Latest Maritime law Articles You Would Like:
Latest News
- What is the Purpose of DG Shipping?
- What are Logistics Risks?
- How Port and Terminal Operators Can Control Emissions?
- Minimum Quantity Commitment (MQC) and Liquidated Damages in Container Shipping: Concept and Relevance
- MARPOL (The International Convention for Prevention of Marine Pollution For Ships): The Ultimate Guide
- The Ultimate Shipping Container Dimensions Guide
Subscribe To Our Newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.
















I am the CEO of sandem logistics and general services a clearing and forwarding agencies in sierra Leone I have learn a lot through this site I would like to learn more about clearing and forwarding.
Best regards
Mitchell Demadinor
@Mitchell: Glad to know the content is useful. stay tuned for more on similar topics.