10 Smallest Aircraft Carriers in the World
An aircraft carrier is usually the capital ship of a naval fleet, allowing it to project its power throughout the world without being dependent on regional bases for handling aircraft operations.
Aircraft carriers are equipped with flight decks and carry arms apart from deploying and recovering fighters, helicopters, strike aircraft, etc. They have evolved a lot from wooden vessels deploying balloons to nuclear-powered ships.
Aircraft Carriers share diplomatic powers and are the centrepiece of a naval force. They have many advantages, such as non-interference with territorial sovereignty and obviating the need for overflight authorisation from 3rd party nations, which decreases the time and transit distance of the aircraft and increases their time in the combat zone.
There are 47 aircraft carriers in 14 navies of the world. Among them, the U.S. has 11, each of which carries 80 fighters, the UK and China each have 2 aircraft carriers, and France and Russia have a single carrier with a capacity of 30 to 60 fighters.
Italy has 2 light V/STOL carriers, and Spain has a V/STOL aircraft-carrying assault ship. Countries like China, the U.S., India, South Korea, Turkey, Russia and France are engaged in constructing more aircraft carriers.
While we have already looked at the biggest aircraft carriers in the world, in another article, let us explore the 10 smallest aircraft carriers mentioned in no particular order.
Chakri Naruebet, Navy of Thailand
HTMS Chakri Naruebet is the flagship of the Royal Navy of Thailand. It is the country’s only aircraft carrier; however, the Navy refers to it as an Offshore Patrol Helicopter Carrier.
Spanish shipbuilder Bazan built it. It was ordered in 1992 and launched in 1996. It was commissioned in 1997, and since then, it has become the smallest aircraft carrier in the world in service.
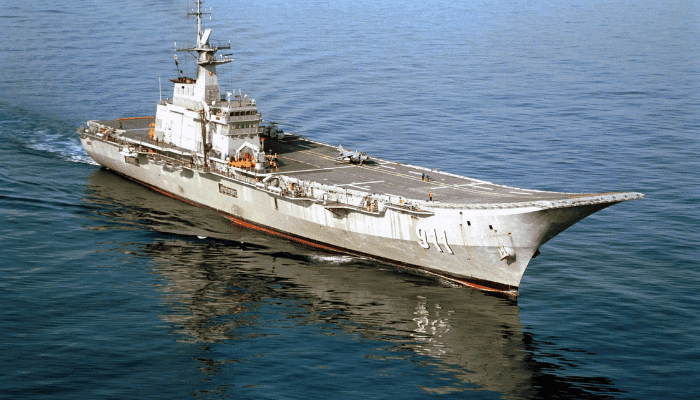

It is 182.65 m long and 22.5 m wide, with a maximum speed of 25.5 knots. Chakri Nauebet has a range of 7150 miles and a complement of 393 sailors, 146 aircrew and 62 officers. It has two .50 calibre machine guns and 3 surface-to-air missile launchers for Mistral missiles, installed in 2001.
It was made to operate V/STOL fighter aircraft groups and helicopters. Chakri Naruebet was made for regular patrols and power projection in the territorial waters; however, lack of finances led to the ship spending most of its time at the Sattahip naval base.
Chakri Naruebet was sent on many disaster relief missions after the 2004 earthquake and tsunami in the Indian Ocean.
Giuseppe Garibaldi, Italian Navy
The 1st through-deck ship ever constructed for the Italian Navy and the first to operate fixed-wing aircraft, Guiseppe Garibaldi is said to be an aircraft carrier. However, it is officially called an aircraft-carrying cruiser.
The 180.2 m long and 33.4 m wide ship has STOVL aircraft and helicopters. It has been involved in operations off the coast of Libya, Afghanistan, Somalia and Kosovo.
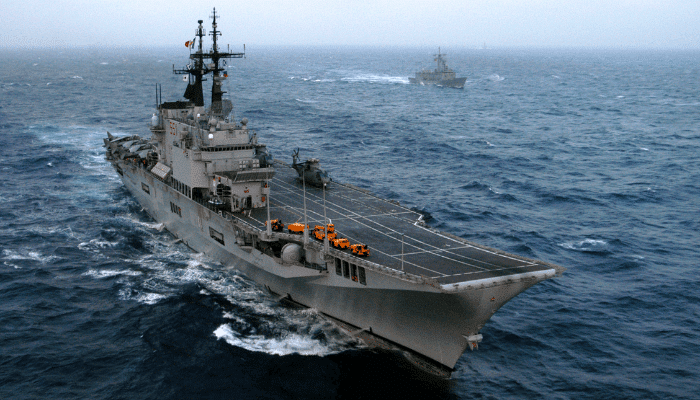
It is the 4th ship of Italy to be named after the famous General Giuseppe Garibaldi and has an image of him on the crest.
The aircraft carrier has a maximum speed of 30 knots and a range of 7000 nautical miles. It has two ILAS three torpedo launchers with triple tubes. It also has 2 SAM launchers for SARH Asphide missiles and 3 Oto Melara Twin 40L70 DARDO CIWS. It also has anti-torpedo systems, decoys, jammers, flares etc.
Its air combat arm comprises 16 AV-8B Harrier IIs, two search and rescue helicopters, and 18 Agusta helicopters.
JS Kaga (DDH-184), Japanese Navy
It is a helicopter carrier being transformed into an aircraft carrier since March 2022. JS Kaga is officially a multi-purpose operation destroyer and the 2nd ship of Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force’s Izumo class. She is named after the Kaga Province in the present-day Ishikawa Prefecture.
This Izumo-class aircraft carrier is 248 m long and 38 m wide with a 7.5 m draft. It displaces 27,000 tonnes when fully loaded and can reach speeds of about 30 knots.
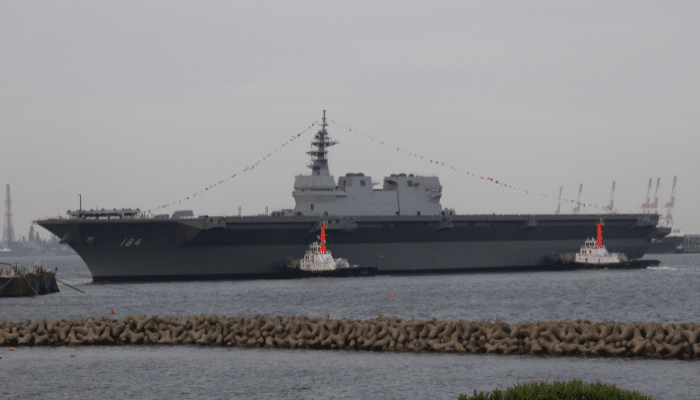

Kaga was one of the first aircraft carriers constructed by Japan since the Second World War ended. It was constructed as a part of the wider Japanese military buildup after increased Sino-Japanese tensions about the contested ownership claims regarding the Senkaku islands.
Kaga can host 28 aircraft or 14 helicopters, and its main objective is fighting enemy submarines, though it is called an operation destroyer by Japan. It can carry 400 troops and also 50 trucks.
ROKS Marado, Republic of Korea’s Navy
Also called LPH-6112, it is the 2nd ship of the Dokdo-class amphibious assault ships of the Navy of the Republic of Korea. It was constructed after making some changes that make it different from ROKS Dokdo, the lead ship of the class.
Its flight deck can accommodate 2 V-22 Ospreys, while Dokdo could carry only one. Marado has Elta Systems EL/M-2248 MF-STAR multifunction surveillance radar and LIG Nex1 SPS-550K 3-D air and surface surveillance radar. It also has different weapons.
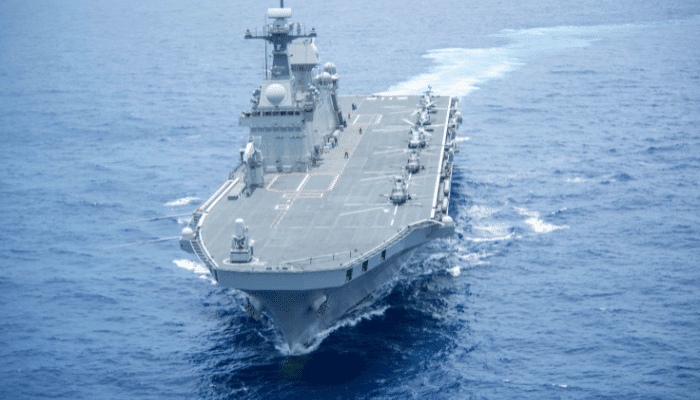

Marado was to enter service quite early in 2010. However, the 2008 economic crisis affected the project, and it was cancelled due to a lack of finances; however, in 2012, it was restored after rising regional tensions.
It was finally launched in 2018 at a yard of Hanjin Heavy Industries & Constructions Co. in Busan. It was commissioned in 2021.
In 2022, Marado participated in RIMPAC along with the Sohn Won-yil-class submarine and Shin Dol-Seok SS-082.
Juan Carlos I, Spanish Navy
It is a multipurpose amphibious assault ship-aircraft carrier in the Spanish Navy. It has a ski jump for operating STOVL and has McDonnell Douglas AV-8B Harrier II aircraft or the Lockheed Martin F-35B II fighter aircraft. The ship was named in honour of the former king of Spain, Juan Carlos I.
This ship has a vital role in the fleet as it serves as a platform for carrier-based aviation, allowing mobility to marines and offering transportation for ground forces.
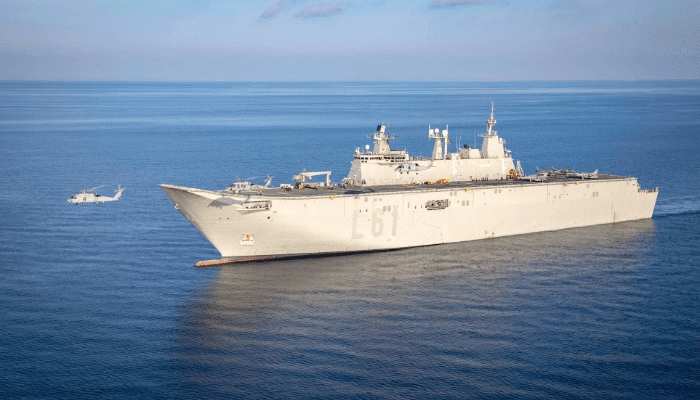

It has a 202 m flight deck and a ski jump ramp. It has 8 landing spots for helicopters and can carry 30 helicopters. It utilises diesel-electric propulsion and has a multifunctional garage and hangar space on 2 levels covering 6000 sq m.
It has a complement of 9000 naval personnel and support elements for 1200. It has a stern-well deck and can carry ground vehicles, too.
Cavour, Italian Navy
This Italian aircraft carrier was built by Fincantieri and launched in 2004. It was designed to combine V/STOL and helicopter air, command and control operations and for the easy transportation of military and civil personnel, including vehicles for the armed forces.
Cavour displaces 27,100 metric tonnes and is 244 m long and 29.1 m wide with an 8.7 m draught. Its 134 m hangar space can also be a vehicle hold for up to 24 battle tanks or even lighter vehicles, numbering about 50.
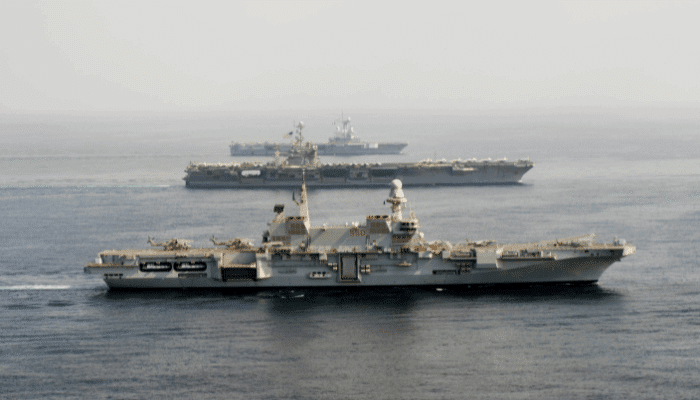

It has access ramps and elevators for aircraft and can also function as a landing platform for heavy transport helicopters and 325 marines.
In 2022, Cavour was a part of training operations with Harry S. Truman, an American carrier ship and Charles de Gaulle, a French carrier. In October 2023, it berthed at Civitavecchia, close to Rome.
HMS Queen Elizabeth, Royal Navy
The lead ship of the Queen Elizabeth Class, HMS Queen, is also the Royal Navy’s Fleet Flagship, which can carry 60 aircraft comprising rotary-wing, fixed-wing, and autonomous vehicles. She was named to honour a World War I era dreadnought named after Queen Elizabeth I.
The aircraft carrier began her trials in June and entered service in 2020. It was made to operate V/STOL aircraft and can engage in airborne early warning and anti-submarine warfare. It can carry 250 marines along with attack helicopters.
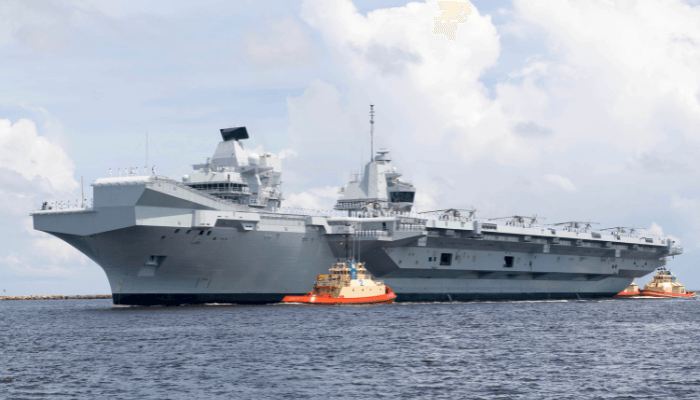

This 284 m long and 39 m wide aircraft carrier is at HMNB Portsmouth. It has a displacement of 65,000 tonnes and has a planned carrier air wing of 24-36 F-35B lightning IIs and 14 helicopters for its first deployment in 2021. It has a hangar below the deck, 2 aircraft lifts, a ski jump and refuelling and re-arming facilities.
It is equipped with Browning .50 calibre heavy machine guns for defence purposes. It is escorted into the high-risk areas by a Type 45 destroyer made especially for this purpose. In less risky situations, a patrol vessel or frigate is used.
MAS Canberra (L02), Royal Australian Navy
It is the first ship of the Canberra-class landing helicopter deck in the Royal Australian Navy. Its construction began in 2008 in Spain, and it was launched in 2011. It was commissioned in 2014, and its homeport is Fleet Base East.
It is 230.82 m long and 32 m wide with a 7.08 m draft. It has the same dimensions as Juan Carlos I, but its island superstructure and internal layout differ, as it was made to meet the Australian Navy’s requirements.
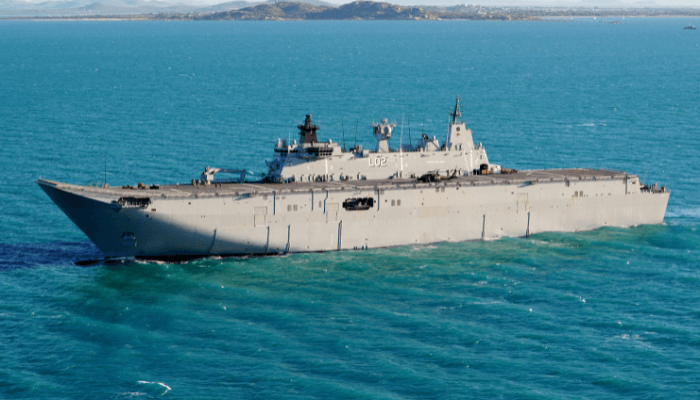

It displaces 27,500 tonnes and can attain a maximum speed of 20 knots. It has a range of 9000 nautical miles and a 45-plus day endurance.
It can easily accommodate 4 LLCs and 110 vehicles since its heavy vehicle deck spans 1410 m2 and light vehicle deck spans 1880 m2. It accommodates a complement of 356 personnel: 293 RAN, 62 from the Australian Army and 3 people from the RAAF.
It is equipped with Giraffe AMB radar, Nulka Missile decoy and many other advanced systems. It can carry 18 helicopters and has a flight deck with a ski jump and 6 deck landing spots.
NAM Atlântico, Brazilian Navy
Amphibious helicopter carrier and the flagship of the Brazilian Navy, PHM Atlantico, was built in the U.S for service with the Royal Navy. She was commissioned in 1998 and served till 2018, after which it entered service with Brazil.
Earlier called the HMS Ocean, this aircraft carrier was bought by Brazil to replace the aircraft carrier Sao Paulo, which was withdrawn from service in 2017 after several mechanical failures.
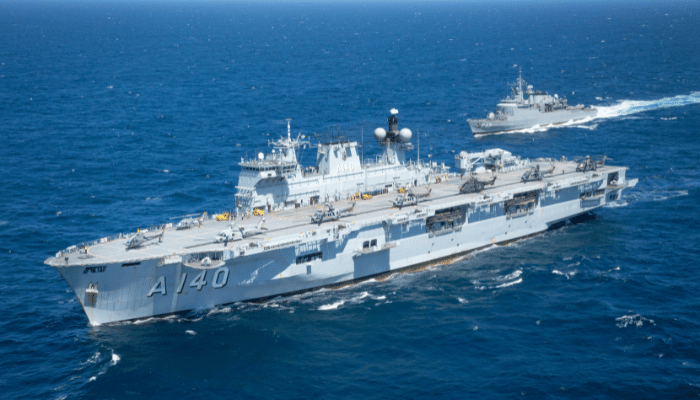

Brazil purchased it in 2018, and it was commissioned into the Brazilian Navy in the same year. Its home port is Arsenal de Marinha do Rio de Janeiro.
It can reach a top speed of 18 knots and has an 8000-mile range. It can carry 40 vehicles and 830 troops, a 285-member crew and 180 aviation personnel. NAM Atlantico has a hangar deck, helicopter lifts and a vehicle deck. It can carry 18 helicopters, including Airbus Helicopters H225M, Sea Hawk, and Airbus Helicopters H125.
INS Vikant, Indian Navy
INS Vikrant is the first indigenously built aircraft carrier of the Indian Navy. It was constructed by Cochin Shipyard Limited in Kochi, Kerela. Vikrant, which means courageous in Sanskrit, is true to its name.
It is 262 m long and 62 m wide with a STOBAR configuration. It can carry 36 aircraft, comprising 26 fixed-wing aircraft, Dhruv MK-III for search and rescue missions, Sikorsky MH-60 R for anti-surface and anti-submarine warfare and Kamov Ka-31 helicopters for airborne early warning.
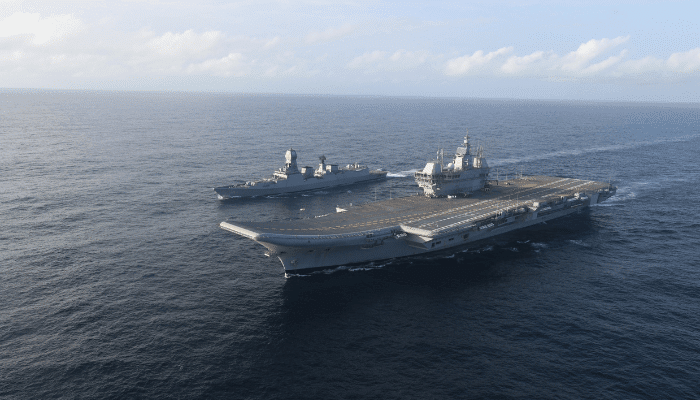
It was commissioned in 2022 and has a maximum speed of 28 knots and an endurance range of 7500 nautical miles.
INS Vikrant has 2300 compartments operated by 1700 naval personnel. It also has a hospital, cabins for female officers, eight generators for electricity supply and 8 km long corridors.
You might also like to read-
- Top 15 Aircraft Carriers in the World
- Top 5 Biggest Aircraft Carriers In The World
- Top 10 Biggest LPG Carriers in The World
- Top 5 Biggest Bulk Carriers In the World
- What Are Nuclear Vessels?
Disclaimer :
The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data or profits arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this website.
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Disclaimer :
The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data or profits arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this website.

About Author
Zahra is an alumna of Miranda House, University of Delhi. She is an avid writer, possessing immaculate research and editing skills. Author of several academic papers, she has also worked as a freelance writer, producing many technical, creative and marketing pieces. A true aesthete at heart, she loves books a little more than anything else.
Latest Maritime Knowledge Articles You Would Like:
Daily Maritime News, Straight To Your Inbox
Sign Up To Get Daily Newsletters
Join over 60k+ people who read our daily newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.















