10 Major Indian Navy Vessels
The Indian Navy is a part of the country’s Armed Forces, with the President being its Supreme Commander. It is commanded by the Chief of Naval Staff and operates in the Persian Gulf, Malacca Strait and the Horn of Africa.
The Blue Water Navy partners with naval forces of other nations for maritime exercises, showing India’s prowess. It also engages in anti-piracy missions, humanitarian work and disaster relief.
Indian Navy Ships are routinely deployed in the South and East China Sea and the western Mediterranean Sea. The main aim of the Indian Navy is to protect India’s maritime borders with the help of other armed forces. The Navy is always ready to face threats or aggression to uphold the nation’s maritime interests.
The Indian Navy has around 67,252 active personnel and 75,000 reserve personnel. It has a fleet of 150 vessels and submarines and 300 aircraft.
Mentioned in this article are the 10 major Indian Navy vessels.
1. INS Vikramaditya
A Kiev-class aircraft carrier, INS Vikramaditya is the flagship of the Indian Navy. It was constructed as Baku and served the Soviet Navy and then the Navy of Russia. However, India acquired it after many negotiations and upgraded the ship, which completed her sea trials in 2013 and entered service the same year.
Said to be one of the biggest ships of the Indian Navy, INS Vikramaditya has an LOA of 284 m and a maximum beam of 60 m, spanning an area equivalent to about 3 big football fields.
It stands 20 storeys tall from its keel to its highest point. The sight of this 44,500-tonne mega steel structure is enough to leave one open-mouthed.
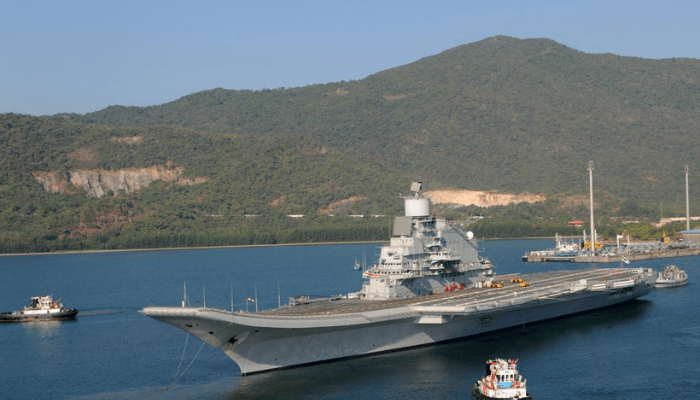

It has 22 decks and around 1600 personnel. It is literally a floating city with an operational range of over 7000 nautical miles or 13,000 kilometres.
The ship can carry more than 30 aircraft, with the MiG 29K swing role fighter being the main offensive platform. It also has advanced launch and recovery systems to enable smooth and efficient launching of aircraft.
It has a Computer-aided Action Information Organisation System providing life into the onboard combat systems. The state-of-the-art LESORUB-E system collects data from the ship’s sensors and presents it as tactical pictures after processing it.
2. INS Vikrant
This aircraft carrier was built in the Cochin Shipyard in Kerala, India. It is named after the country’s first aircraft carrier, INS Vikrant. Vikrant translates to brave in Sanskrit and aligns with the ship’s motto, ‘I Deafeat those who fight against me’.
The aircraft carrier is 262 m long and 62 m broad, displacing about 45,000 tonnes. It has a top speed of 28 knots and an endurance of 7500 nm. It has 2300 compartments operated by 1700 seamen. It also has a hospital, cabins for female officers, corridors spanning 8 kilometres and 8 generators that can light a city of 2 million.
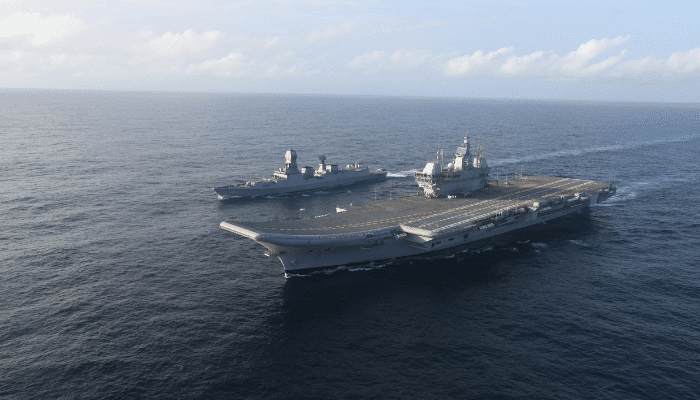
Work on INS Vikrant began in 1999, and its keel was laid in 2009. It was launched in 2013 and completed trials in 2020, with sea trials ending in 2021. It was finally commissioned in September 2022. Flight trials of its aircraft will be completed this year. The project cost 23,000 crore at the time of sea trials, which is about US$3.2 billion.
It can carry an air group comprising 36 aircraft and has a STOBAR configuration along with anti-surface and anti-submarine warfare abilities. It can also conduct search and rescue operations.
Its CMS was developed by Tata Advanced Systems, making it the first combat management system made for the Navy by a private company.
3. INS Chakra
INS Charka is a 111 m long and 13 m wide nuclear-powered attack submarine of the Indian Navy. The construction of this sub began in Russia in 1993; however, work was halted due to a lack of funds. India sponsored its further construction and trials if it was leased to the Indian Navy for the next decade.
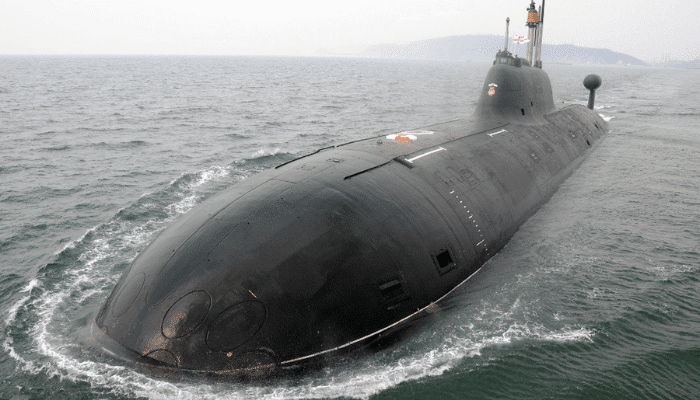

This submarine was launched as K-152 Nerpa in 2008. While it was undergoing its trials in the Sea of Japan in 2008, its fire suppression system was activated accidentally, which led to the deaths of 20 civilian specialists and crew while 41 were injured.
It finally entered into service in 2009 with the Russian Navy. It was leased to India in 2011, and after many trials, it was commissioned into service as INS Chakra at a ceremony held on April 4, 2012.
INS Chakra was returned to Russia in 2021, ahead of the 10-year lease expiry, possibly because of its unreliable powerplant and issues with maintenance apart from its overall condition. The Indian Navy used it to train crew of naval submarines. Nonetheless, it was a major vessel of the Indian Navy.
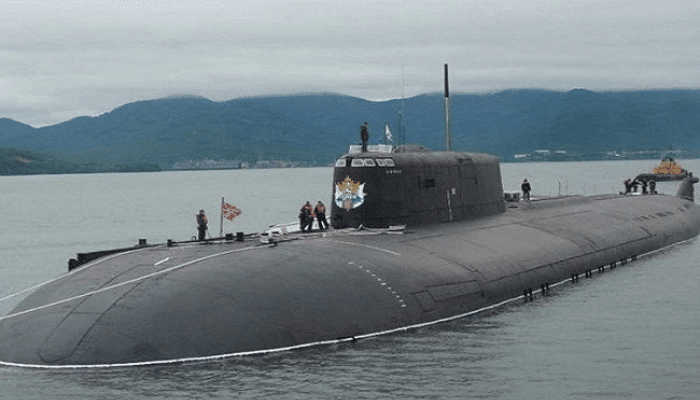
4. INS Arihant
INS Arihant (SSBN 80) is a nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine and also the lead ship of her class. After it was launched on 26 July 2009 by the then PM Manmohan Singh, it was sent for sea trials on 23rd February 2016 and was commissioned the same year. She was deployed in 2018.
It was announced on 5 November 2018 that INS Arihant had completed its first 20-day-long deterrent patrol the previous day. The 6000-tonne ship was constructed as part of the Advanced Technology Vessel Project at the Ship Building Centre in the Indian Port city of Visakhapatnam.

/ x.com
Its hull was constructed by L&T’s Hazira, while Tata Power Strategic Engineering Division designed the control systems. Russia aided a lot by offering assistance to scientists in reducing the reactor so it could fit into the submarine’s hull.
Arihant is 111 m long and has a 15 m beam with a speed of 24 knots when submerged. It can carry 95 to 100 officers. It has four vertical launch tubes to carry 12 smaller K-15 or four bigger K-4 missiles.
5. INS Kolkata
INS Kolkata is a part of the Kolkata class, also known as Project 15 A, of the guided-missile destroyers built for the Indian Navy. This class has two more ships- Kochi and Chennai, all constructed by Mazagon Dock Limited.
They are said to be one of the biggest destroyers operated by the Indian Navy. INS Kolkata is said to be the most potent warship made in India. It measures 164 m lengthwise and has a width of 18 m with 7400 tonnes of full load displacement. INS Kolkata has a complement of 30 officers and 300 sailors.
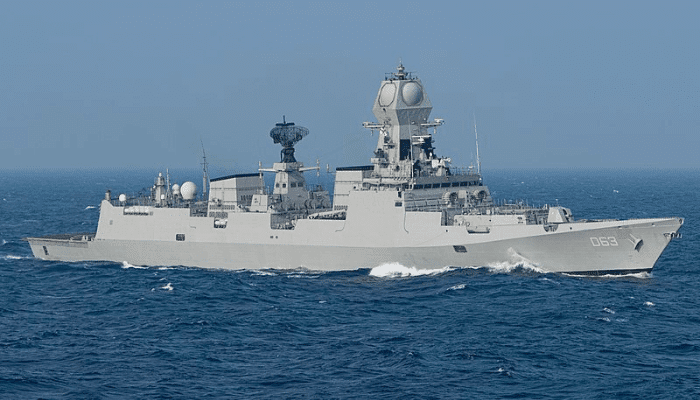

Construction delays and extended sea trials pushed the commissioning date of the first vessel from 2010 to 2014. Several issues, such as additional noise when the engine, shaft and gearbox functioned together, also led to delays.
The INS Kolkata and the other two ships of this class are a modified and a better version of the Project 15 Delhi-class destroyers in terms of major design improvements, additional land-attack capacity, modern sensors and advanced weapon systems, and extended use of Cooperative Engagement Capability.
The vessel has a Combined Gas and Gas propulsion system with four reversible gas turbines that can attain a speed of 30 knots. It can produce enough power to light a small town.
6. INS Delhi
INS Delhi is a guided-missile destroyer of the Indian Navy, a part of the Delhi class of destroyers. She was constructed at Mumbai’s Mazagon Dock Limites and was commissioned in 1997.
She is 163 m long and 17 m wide with a draught of 6.5 m and a displacement of 6200 tonnes. She has a complement of 350, including 40 officers.
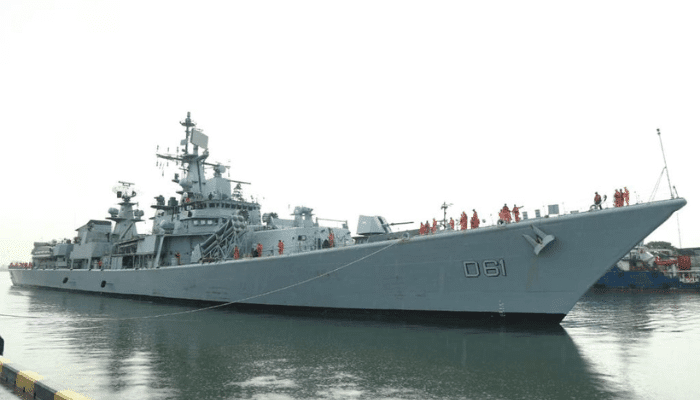

INS Delhi underwent upgrades from 2018 onwards, and in 2022, she entered service again with advanced sensors and a new Modular Launcher for the Brahmos Missile, whose tests were done onboard the ship in April 2022.
The ship has been involved in many important missions, such as in 2009 when it was deployed to Europe and participated in naval exercises with the French Navy and the Royal Navy.
In 2020, the ship underwent refitting again, including upgrading many weapons and sensors. One major upgrade was the addition of BrahMos Missiles, which were already sanctioned in 2015. Its electronic warfare system was changed to Ellora Mk II with Kavach launchers. Even Atlas Elektronik ACTAS sonar was also installed.
7. INS Satpura
The 6000-tonne stealth frigate hailing from the Shivalik-class is meant to seek and destroy enemies in airways, on the surface and undersea. INS Satpura is a part of the Eastern Fleet, headquartered at Visakhapatnam.
It is endowed with advanced stealth and land attack weapons. It was constructed in Mumbai at the Mazagon Dock Limited, and its keel was laid in 2002. It was launched in 2004. The ship’s construction ended in 2010, and it underwent sea trials before being commissioned in the Navy in 2011.
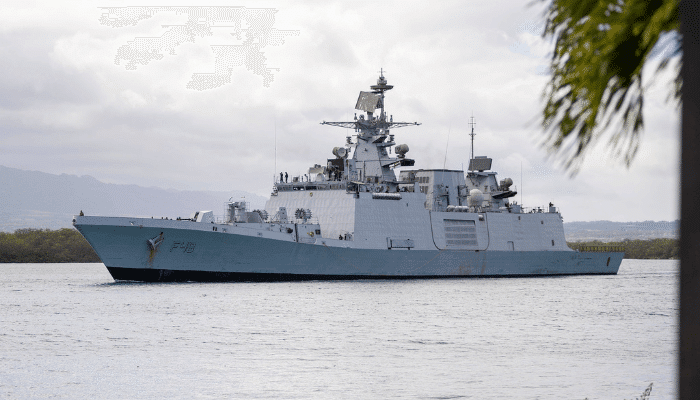
Named after the famous mountain range in India, the Satpura Range, this ship’s motto is Determination, Pride and Bravery, which it has always shown in all its missions and deployments until now.
The 142.5 m long and 16.9 m wide ship with a 4.5 m draught was deployed to the South China Sea and the Western Pacific Ocean in 2016, where it took part in the RIMPAC exercise with other naval vessels.
8. INS Talwar
INS Talwar translates to Sword in Hindi and is the lead ship of the Indian Navy’s Talwar class of frigates. It is the frontline warship of the Navy’s Western Fleet.
She was constructed in Russia, and while most of the equipment onboard the vessel was made in Russia, many onboard systems are of Indian Origin.
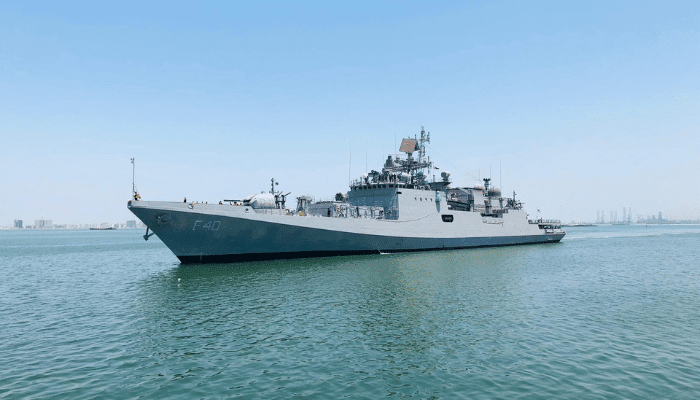

Her sea trials were completed in 2002, and she was commissioned into the Navy in 2003. She is 124.8 m long and 15.2 m wide and has a 4.5 m draught. She has a displacement of 3620 tonnes and can attain a speed of 30 knots. She also has a complement of 180, which includes 18 officers.
She is a multirole frigate and has been a part of several missions and operations since entering service, including anti-piracy operations off the Somalian coast.
She was also stationed in the Indian Ocean and visited several ports. She participated in the Malabar 2008 exercise with the U.S. Navy and recently the Cutlass Express 2021 exercise with the French Navy.
9. INS Kamorta
It is an anti-submarine stealth corvette from the Kamorta Class, constructed for the Indian Navy. INS Kamorta was designed and built by GRSE. It was launched in 2010 and named after the Island of Kamorta in the Andaman and Nicobar.
Kamorta is 109 m long and 13.7 m broad. It displaces around 3500 tonnes when it is fully loaded. Powered by four diesel engines, this ship was commissioned in the Navy in 2014.
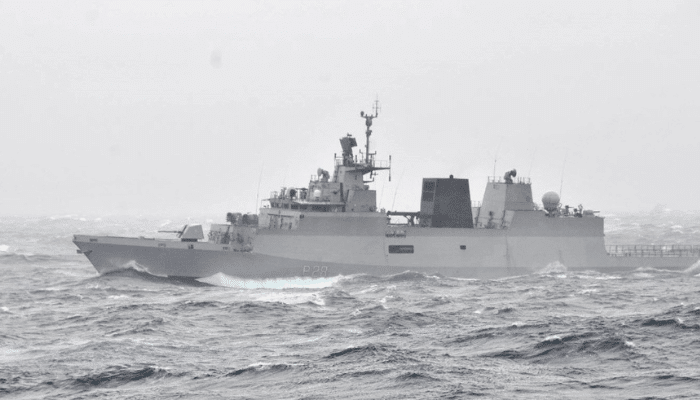

It can attain a speed of 32 knots, has a complement of 180 seafarers and 15 officers apart from flight crew for ASW helicopter, and an endurance of 7400 kilometres.
Made from top-quality steel, she has an array of weapons, such as main guns, missiles, anti-submarine rocket launchers, and tubes for firing torpedoes.
It has a mounted sonar system and an indigenously developed radar surveillance system called Revathi, which can find targets exceeding 200 kilometres. It was also the first ship to have the Kavach decoy system to protect against anti-ship missiles.
10. INS Saryu
INS Saryu is the biggest offshore patrol vessel in the Indian Navy. It was built in the country by Goa Shipyard Limited and is homeported at Port Blair, part of the Andaman and Nicobar Command. It will engage in offshore surveillance and patrol Indian exclusive economic zones and sea lines of communication. She also engages in anti-piracy patrols and fleet-support operations.
She belongs to the Saryu class of patrol ships ordered by the navy for coastal patrol operations in 2008. Saryu was constructed for three and a half years for US$ 78 million.
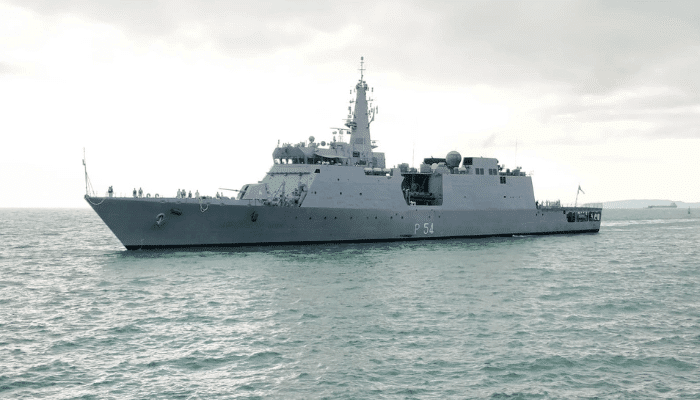
It has a 6000 km range and can remain at sea for two months without requiring to come to shore for replenishment. She is manned by 8 officers and 105 sailors and is equipped with guns, advanced weapon systems, chaff launchers, early warning and navigational radars, electronic warfare systems, etc. She has two inflatable motor boats and a multi-role helicopter.
She has an automated power management system; power and propulsion can be managed through a remote-control system. An integrated LAN and CCTV management system increases crew efficiency and enables optimum utilisation of its equipment.
The 2300-tonne ship is 105 m long and 12.9 m wide. It has 2 SEMT Pielstick diesel engines, the biggest engines in the Indian Navy, allowing it to attain over 25 knots.
You might also like to read-
- INS Vikramaditya – The New Air Craft Carrier of Indian Navy
- INS Viraat – ‘Mother’ Air Craft Carrier Of Indian Navy
- INS Satpura: The Indigenous Shivalik Class Stealth Frigate of Indian Navy
- Merchant Navy Recruitment Process – Entrance Exam, Salary And Jobs
Disclaimer :
The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data or profits arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this website.
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Disclaimer :
The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data or profits arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this website.

About Author
Zahra is an alumna of Miranda House, University of Delhi. She is an avid writer, possessing immaculate research and editing skills. Author of several academic papers, she has also worked as a freelance writer, producing many technical, creative and marketing pieces. A true aesthete at heart, she loves books a little more than anything else.
Latest Maritime Knowledge Articles You Would Like:
Subscribe To Our Newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.















