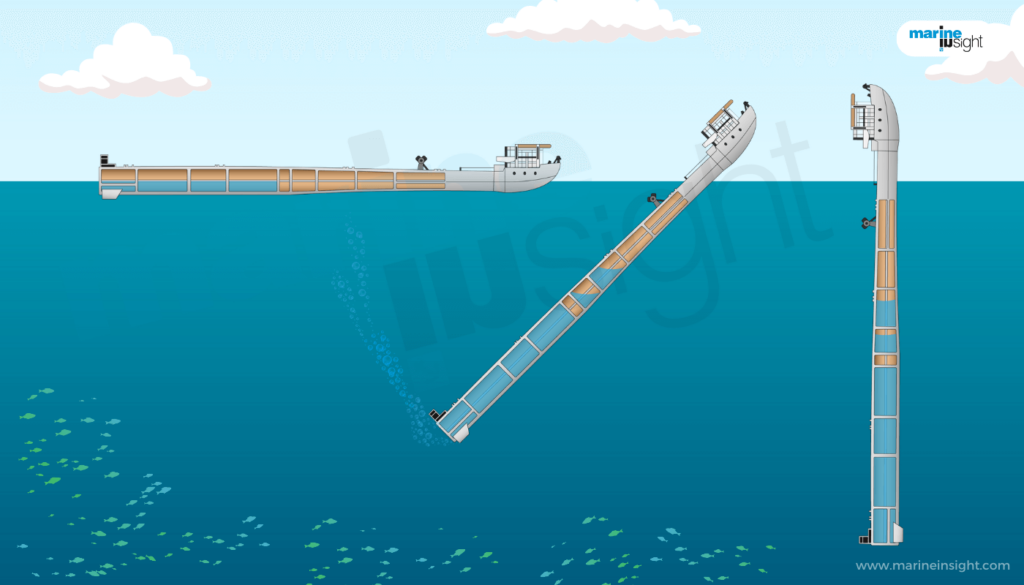
Different Types of Dredgers Used in the Maritime Industry
A marine vessel fitted with a device(s) to scrap or suck the sediment deposition over a sea bed is known as a dredger (The device used for excavation and scraping of the sea bed is called the Dredge).
In a more general sense, a ship equipped with an excavation tool that is capable of weeding off depositions such as sand, gravel, sediments, etc. from the seabed is referred to as a dredger ship or more commonly a dredger.
Dredgers are of great importance, as they serve the purpose of ensuring the necessary safe bottom clearance for safer voyages.
The excavation carried out in either shallow or fresh waters with the aim to gather up the sediments located in the bottom to dispose of at another place is called Dredging.
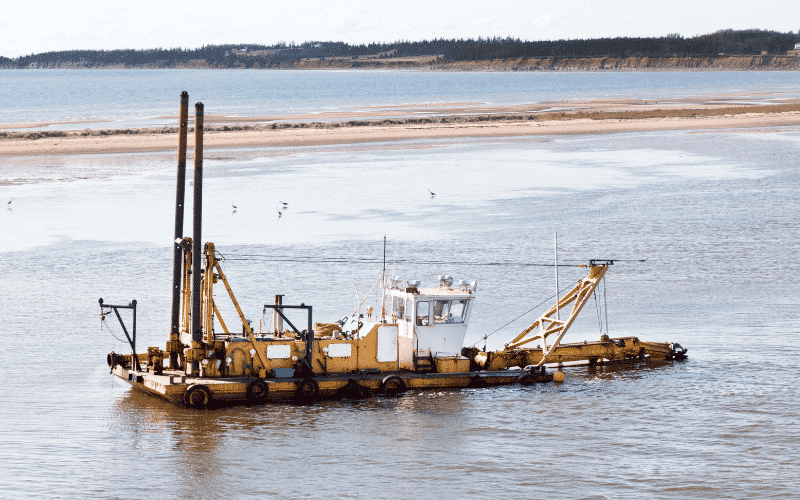

The sediments might be gathered for purposes like:
- making water navigation or fishing easier in shallow waters
- for replenishing the sand on public beaches which might have undergone severe coastal erosion
- Gold and coal mining
- Removal of contaminants from the sea bed
- Reclamation of areas damaged by oil spills or natural calamities
- Creation of new harbours
Although dredging can have very harmful effects on the marine and aquatic environment, in some situations it may be the only option available.
Broadly the types of dredgers are classified into three categories (On the basis of the method employed for transportation, of dredged material from the bottom of the sea to the surface of the water):
- Mechanical dredgers which are suited for working in confined areas and are useful for removing the hand-packed material or debris,
- Hydraulic dredgers work on the principle of adding large amounts of process water to change the original structure of the sediments, and
- Other dredgers do not fit into the above two categories.
Related Read: Cristobal Colon: The Largest, Hi-tech Ocean Dredger
Whether mechanical or hydraulic, the different types of dredgers that help in the removal of the seabed sediments are:
1. Mechanical Dredgers:
These are available in a variety of forms, but each has the same working principle of “hand-packing”. These are equipped with a grab or a bucket, which is driven on the loose bed sediments, then material get filled in the bucket and the bucket is then raised to transport it to the requisite disposal site. Some common mechanical dredgers are briefed as follows:
(i) Bucket Dredgers:
These are the oldest type of mechanical dredgers. These are fixed on anchors so considered as stationary dredgers but can be moved along the semi-arcs while dredging, with the help of winches.
An endless chain of buckets is provided in bucket dredgers, these buckets scrap off and fill the loose dredged material in them and after being completely filled, these buckets can be emptied into barges by turning the bucket upside down over the barges.
(ii) Bucket Ladder Dredgers:
These kinds of dredgers are just modifications of conventional bucket dredgers, the series of buckets used in these dredgers are mounted on a wheel that mechanically picks up the sediments. They are more efficient and can be used to rip out even powerful and hard corals. The only limitations of these dredgers are their low production, the requirement of more anchor lines and high level of noise, which made them obsolete these days.
They can be used for a wide variety of materials including soft rock material and are powerful enough to rip out the corals as well. But because of their low production, high level of noise and the need for anchor lines, their use has hugely diminished in recent times.
(iii) Grab Dredgers:
Grab Dredgers (or Clamshells) are also stationary dredgers fastened either on anchors or on spud-poles. The cutting tool, of these dredgers, is a grab that consists of wire operated two half-shells.
Related Read: How Dredging Anchor is Used for Maneuvering Ships?
These half-shells after filling dredged material in them, load the material in barges. Grab is mounted either on a dragline or hydraulic excavator. These can be of different types such as (top) open grab, (top) closed grabs and watertight grabs.
Grab dredgers can be of different capacities ranging between 1.0 and 20 m³ whereas the capacity of grab hopper draggers ranges from 100 to about 2,500 m³. Their capacity largely depends upon the crane power. Grabs are efficient in removing material in corners of dock and basins and also these make excavation closer to quay walls easier.
A revolving crane, fitted with a grab, placed on a hopper vessel or pontoon is known as a grab dredger. As the name suggests, it picks up the sediments at the seabed with a clam grabbing motion and discharges the contents. Often used for excavating bay mud it also is useful to pick up clays and loose sand.
(iv) Backhoe Dredgers:
These are also referred to as Dipper dredger and are somewhat similar to onshore excavators. These are used for harbour maintenance and shallow dredging. These are hydraulically driven excavators and consist of a half-open shell or a digging bucket which is capable of digging across a wide range of materials.
The shell or bucket is moved toward the machine and when filled, emptied in barges. Bucket capacity ranges between 0.5 and 13 m³. Care should be taken while dropping this heavy and rigid bucket as it can cause damage to canal lining or quay walls.
Like some onshore excavators, Backhoe dredgers have a digging bucket attached to it which digs through a wide range of materials and when it is excavated it’s brought out and placed on the onboard barges. Although they have few limitations where deep dredging is concerned but with some recent modern dredgers, deeper excavation is made quite easy.
Related Read: Ravestein Builds The Largest And Most Efficient Backhoe Dredger For Boskalis
2. Hydraulic Dredgers:
The key feature of hydraulic dredgers is that the material dredged by these type of dredgers is in suspension form and raised through the pumping system and fed to outlet pipes.
These are most suitable for dislodging fine materials because it is easier to hold fine materials in the suspension than heavy gravels.
Gravels and other powerful material can also be removed through hydraulic dredger by using greater power pumps. Some common hydraulic dredgers are as under:
(i) Suction Dredgers:
These are generally employed to remove sand or silt deposits from the seabed. They have a vertical suction pipe, which is pushed vertically inside the sand deposit and dredged material is sucked with or without water jet. The dredged material is laden into barges or can directly to the reclamation area.
These suction dredgers can be of two types viz. profile or plain suction Dredgers and Cutting Suction Dredgers. Rest of the working and design of cutter suction dredger is similar to the plain suction dredger but has the only difference that cutter suction dredger is equipped with a cutting tool which may be swinging arc.
CSD, as they are normally called, have a cutter head at the suction inlet which helps to loosen the earth and take it to the suction mouth. Used for hard surfaces like rock, CSDs suck up the dredged soil with the help of a wear-resistant pump and then discharge it through a pipeline or a barge.
(ii) Trailing Suction Hopper Dredger:
A Trailing Suction Hopper Dredger is a self-driven dredging vessel. It consists of hoppers or trailers with bottom gates or valves. The material is loaded in hopper hydraulically when this hopper or trailer is filled, the bottom valves or gates are closed and the hopper is raised up with cranes or winches. This dredger is most commonly used in open water: rivers, canals, estuaries and the open sea dredging.
Related Read: Video: World’s Third Biggest Trailing Suction Hopper Dredger
Suitable mostly for harbour maintenance and pipe trenching, a hopper dredger is a self-propelling vessel that holds its load in a large onboard hold knows as the hopper. They can carry the load over large distances and can empty it by opening the bottom doors or by pumping the load offshore. Hopper dredges mostly dredge the soft non-rock soils and because of their high production rates can carry out land reclamation projects easily.
(iii) Water Injection Dredger:
It is a self-driven dredger that excavates sediments with strong water jets. Strong water jet converts the sediments into suspension, as this suspension is heavier than water, it is carried away by water currents and gravity and disposed-off at a specific site. This type of dredger is generally used to dredge mud or fine sand bottoms and are more commonly used for harbour maintenance.
Often used for environmentally sensitive projects, water injection dredgers work by fluidizing the material by pumping water into the bed material. Once it is fluidized it is either moved by a second burst of water or is carried away by the natural current.
Related Read: Effects of Dredging on the Marine Environment
3. Other types of dredgers:
These are the dredgers which don’t fall in the category of hydraulic and mechanical dredgers but are designed for a specific purpose. All these other types of dredgers are operable in shallow waterways such as narrow canals, industrial lagoons and reservoirs. They include:
(i) Jet-lift dredgers and Air-lift dredgers:
Jet-lift dredgers work on the principle of Venturi effect. A high-speed stream is injected, which in turn pushes the adjacent water along with the bed material, into a delivery pipe.
Air-lift dredgers are similar to jet-lift dredgers with the only difference that high-pressure air is used as the medium for inducing water or material and dispose off through suction pipe. These jet-lift dredgers, as well as air-lift dredgers, cannot be used for powerful and hard material.
(ii) Augur suction dredgers:
These dredgers work on the outline of mechanical cutter suction dredgers, except that these dredgers are equipped with a rotating Archimedean screw for cutting, which is placed perpendicular to the suction pipe. The augur like screw rotates and removes material, after removal the material is served to the centrally placed suction pipe. This dredging method is employed where the material is to be dredged in precise vertical as well as horizontal dimensions.
(iii) Reclamation Dredger:
This type of dredger is generally used for reclamation purpose. These are also referred to as barge unloading dredgers.
(iv) Pneumatic dredgers:
These work on the same principle as a vacuum does. They consist of a chamber with high vacuum pressure inside and the chamber is suspended with the help of a crane. Bed material is pumped in the inlet chamber through vacuum pressure and the chamber is lifted up through crane and emptied at the requisite site. These types of dredgers are opted only for easily flowing material.
(v) Amphibious dredgers:
These are a result of great technical advancement as these are capable of working in both submerged as well as in raised condition. These are equipped with grabs, buckets or a shovel installation to carry out the dredging.
(vi) Plough or bed leveller:
It is a special type of dredger which has a long cutting blade or bars fixed with a boat. As the dredger move over the bed, it scrapes off the bed level to the requisite depth. It is used for short length direct dredging, as it simply scraps the dredged material with a blade to a certain distance.
Over to you..
Do you know any other
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of Marine Insight. Data and charts, if used, in the article have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and Marine Insight do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendation on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and Marine Insight.
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Latest Type Of Ships Articles You Would Like:
Subscribe To Our Newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.













What are the average charter hire for Backhoe Dredgers ?
can a dredger be used for the extraction of sand from rivers for construction?
I recently noticed that it is difficult for my boat to enter the dock because it looks like there is a build up of sediments, so I am thinking about hiring a spot dredging company. I had no idea that there are so many different types of dredgers and yo make a great point that trailer suction hoppers are typically best for harbor maintenance. The fact that they have a high production rate gives me peace of mind that it would be a fast and painless process. I will definitely ask potential companies about the type of equipment and dredgers they use before hiring them.
The party boats that I assume that you are refering to are like the smaller ponton boats that have two long tubes on them that has a flat deck with railing around them and an outboard, cooler and BBQ on the deck. Not really fast, but a fun way to spend the day/evening.
i need the dredges work for bangladesh
Hello Sir, I just want to know to more about 1) jet lift dredgers, air lift dredgers and Pneumatic dredgers with some pics if any with you. Thanks and regards, Tansi Noronha.