10 Types of Ship Disposal Techniques
Every type of ship comes with a specific lifespan. After serving a successful tenure at the sea (a tentative period of thirty years or so), all ships are expected to be discontinued from service according to the maritime law. The disposal of ships, after having ruled oceanic waters, has been carried out since the early days of shipping. Ship disposal in early days meant that ships were just left unattended which lead to the making of some of the biggest shipyards in the world.
Ship disposal methods have come a long way. Several methods have been utilized and discontinued in the past. Today, disposal of ships is a great concern for ship owners as it requires substantial money and efforts. Several guidelines have to be followed to ensure that the disposed material is not causing any kind of threat to environment or human life. Moreover, before the ships are reduced to mere scraps of steel, it’s mandatory to eradicate any toxic substance present in them. As ship breaking is costly in developed nations, some of the developing countries of Asia has become ship breaking hubs of the world.
Few environmental administrative bodies like the Basel Convention, set down specific guidelines and regulations for the ships which are declared to be obsolete and ineffective. The main objective of these guidelines is to maintain the safety and harmony of nature while a vessel is being cast away. The retiring ship needs to be disposed of, in an eco-friendly strategy which would not affect the environment in any serious manner.
Taking the above mentioned points into consideration, several ship disposal techniques have been used until now. Some of the main types of ship disposal methods are mentioned below:
1. Shipbreaking on Beaches
Shipbreaking – the most common method of ship disposal is also considered as one of the most life-threatening jobs in the world. Beaching of ships is done to carry out this process. Ship Breaking includes tearing down of the ship on dedicated ship breaking beaches. Thousands of tonnes of steel is scrapped and disposed off by workers using minimum tools and safety precautions. The process involves high-risk possibilities that have resulted into deaths of several unfortunate laborers in the past. In spite of several problems faced by such ship breaking yards, they are a thriving business in many Asian Countries such as India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh.
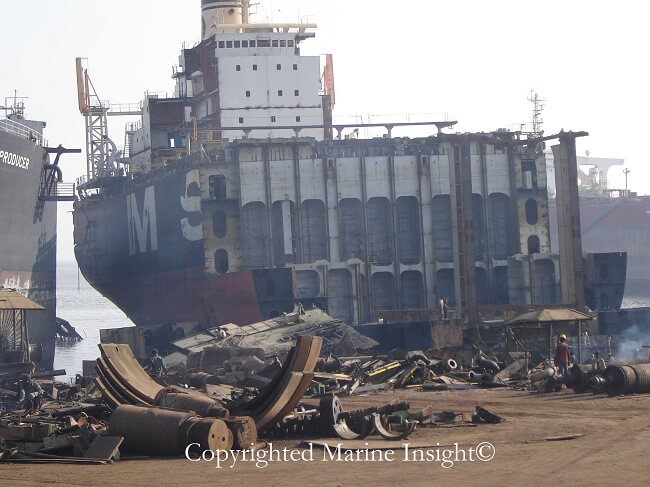

Several toxic ships are scrapped in these ship breaking yards, as workers continue to face threats from serious hazardous substances during ship disposal.
2. Domestic Ship Recycling
The aim of the Maritime Administration of any country is to recycle those vessels that pose an immediate threat to the ecosystem. For this, the committee ensures that it collects adequate funds for the disposal techniques. Domestic ship recycling thus involves breaking of ships so that its parts can be used again. Domestic ship disposal can be exhibited through vessel sales offers and fee-for-service solicitations. Such programs can even present ship recycling contracts as prestigious awards to “recyclers” that aim at reusing the domestic vessels.
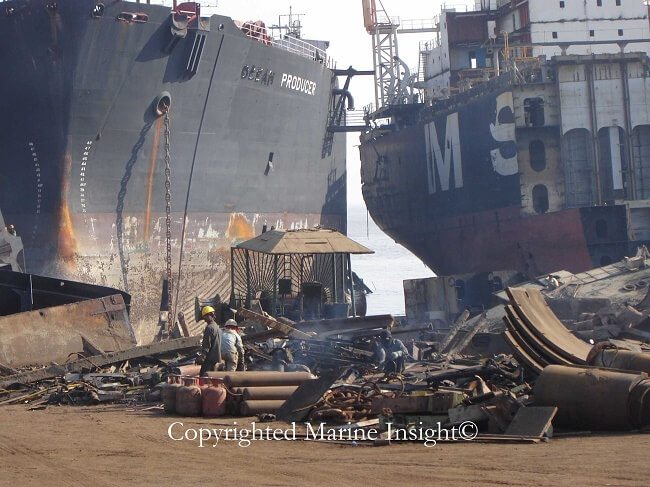

According to statistical records, over thousand retired vessels are collapsed and reprocessed in a single year. Essential raw materials can be extracted from the old ship parts and machinery, constituted of steel and other metals. As mentioned earlier, a majority of ship disposal sites are located in the perilous regions of South Asia, which might involve occasional tidal wave attacks in the coastal areas.
3. Artificial Reefing
On many occasions, artificial reefs are created by drowning the disposable ships in deep water, offshore. Precautionary measures are undertaken to ensure that the disposable vessel is devoid of any hazardous elements or electrical devices, before it is compelled to sink.
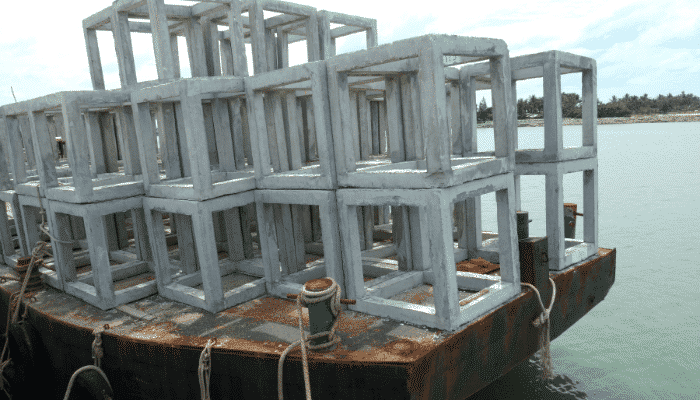

These man-made reefs offer a secure habitat for innumerable species of the marine world. The artificial reefs are used to provide food and shelter to the fishes, and also aid in promoting the spawning prospects. Such ship disposal technique is used in several countries.
4. Hulking
This process of ship disposal ascertains that the hull of a disposable vessel stays unaffected in water, while other functional ship parts are not kept intact. The particular ship hull can float in the water but it does not participate in sailing. For this it is extremely necessary to eliminate all kinds of toxic chemicals before a ship hull is allowed free existence and is employed for a different purpose, once its navigation tenure is over. The painted hulls have a tendency to rot in the water, which would cause an unavoidable discharge of unwanted chemicals.
5. SINKEX
The deep water sinking method for ship disposal is also referred to as SINKEX – Sink Exercise, or even as HULKEX (Hulk + Exercise). Like other ship disposal processes, this also needs the absence of hazardous components from the concerned vessel, lest they pollute the environment. Moreover, added precautions are taken on to prevent the underwater marine life from any damage and to check that the ship has been permanently cast away on the ocean bed.
The SINKEX ship disposal technique involves a fire-shooting exercise conducted by the Navy to rehearse and train in weaponry, missile practicing, torpedo accuracy etc. The target ships are useful in warfare training sessions where these are deemed as targets for shooting. The practice ships are blasted into pieces by using military torpedoes, which eventually leads to sinking of ship and its disposal. This is an effective way to test military weapons without damaging new vessels. The Navy gets hold of a live target training session, while the unused ships are efficiently turned into a pile of waste. According to records, the US Navy conducts the SINKEX operations in remote regions of Hawaii, Kauai, California coast and Puerto Rico.
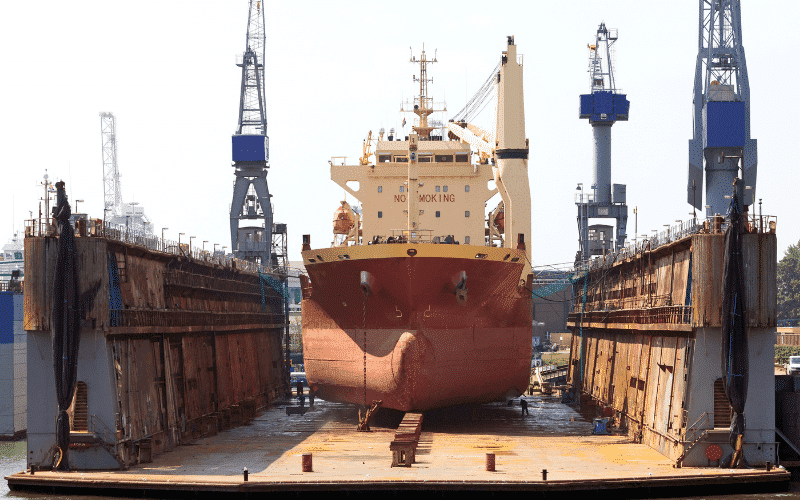
6. Ship Breaking in Dry Docks
This ship disposal technique aims at dismantling a vessel in a ship dock. This is the safest and cleanest method of ship disposals as the process takes place in dry docks. Though such technique provides zero chance of accidental pollution, the method is extremely expensive.
7. Memorial Ships/ Ship Museums
Ship museums are naval vessels with historical significance which serve as memorials, after they have finished their sailing tenures and are now rendered ineffective. The museum ships help to cater to the educational needs of people, and also display history in the most authentic manner, which is also fun and interesting for the viewers.
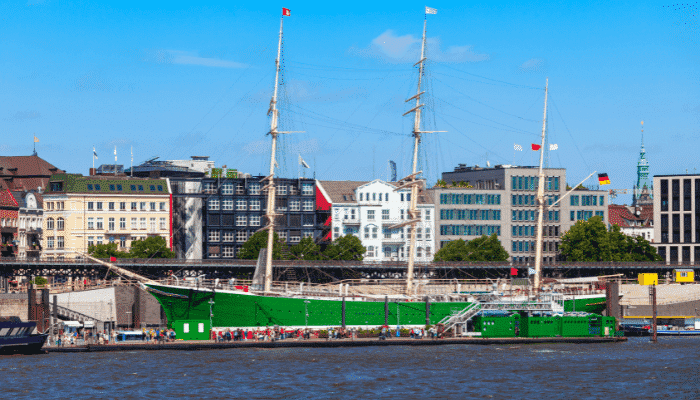

The old vessels are themselves epitomes of fearless warfare and unsung heroes, and are rewarding to the memories of the brave sailors. There are several museum ships around the world which form a unique ship disposal method.
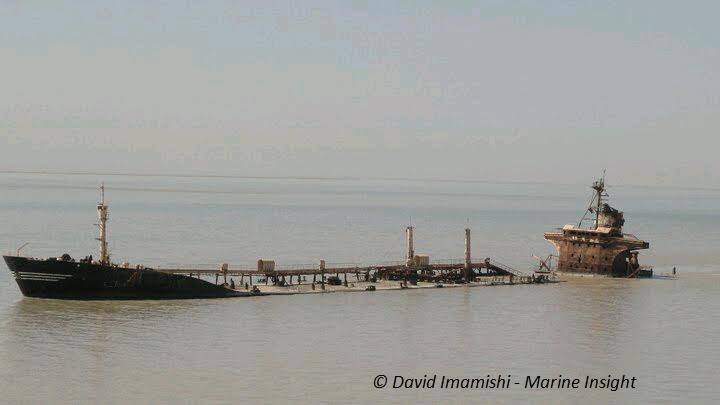
8. Scuttling
Scuttling ship disposal is a common method of deliberately drowning an abandoned or retired vessel, by allowing water to fill up its hull by opening the ship valves or through creating holes in the ship with the help of explosives.

9. Wreck Diving Sites
Wreck diving sites are artificial ocean diving sites that are created by sinking unused vessels, on purpose. The shipwreck might serves as a training place for divers or may acquire commercial revenues by allowing recreational diving facilities. Before ship disposal, it needs to be free from all sorts of hydraulic liquids, oils, and harmful toxins like PCBs.
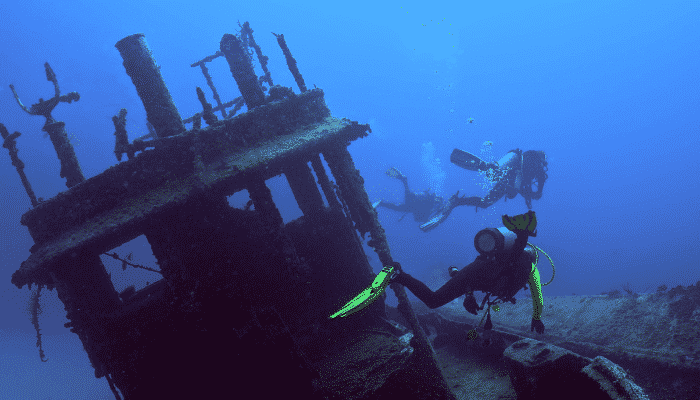
In fact, the greater portion of the vessel’s superstructure is isolated to prevent it from water erosion. While the ship is being purged of hazardous chemicals, essential materials such as the copper wiring may be used to draw the expenses required for preparing the ship for sinking.
10. Ship Donation Program
The Ship Donation Program by Maritime Administration of US was started in the year of 2004, according to Public Law 108-136, Section 3512. As a consequence, many public or non-profit establishments acquire the chance to receive numerous disused vessels as a method of ship disposal. These obsolete ships from the National Defense Reserve Fleet (NRDF) can be preserved as memorials or can find further application in non-commercial activities. This program is mainly reserved for ship disposal of naval vessels of historical significance.
You may also like to read – Legal Issues And Arrest Of Scrap Ships Can Sour Deals For Indian Cash Buyers
References: spiegel, marad, artificialreefs, imo, priyablue
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Latest Shipboard Guidelines Articles You Would Like:
Subscribe To Our Newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.















