What is a Bearing Scraper?
A bearing scraper is a precision tool with multiple sharp-edged blades. It is operated by hands to level out high spots on soft metal engine bearings.
As the plane and smooth bearings offer advantages over rolling elements, scraping comes into an influential role.
The scraping process is aimed at achieving the correct geometrical alignments by evenly spreading the points of bearing contact.
Scraping is the only procedure to sculpt flat straight surfaces evenly across the length and width of their mating surfaces in cast iron, of which, most types of machinery are built.
Marine Bearings namely the main bearing, top-end bearing, bottom end bearing, thrust end bearing and pedestal bearing are vital parts of the ship for the following roles:
- To allow relative motions and ensure perfect alignment.
- Transmission of heavy load.
- Removal of heat that is generated due to friction.
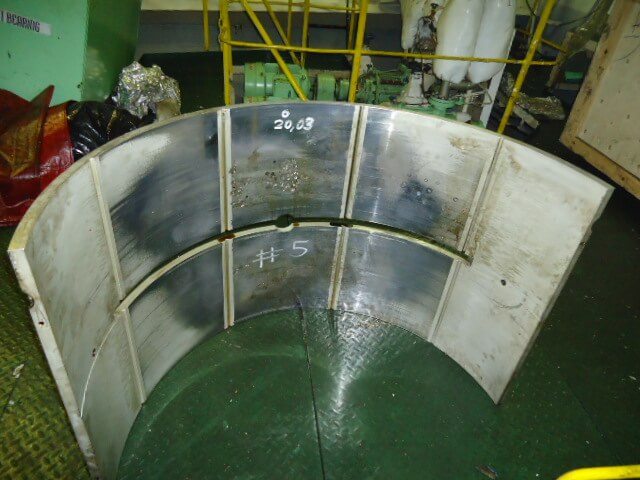

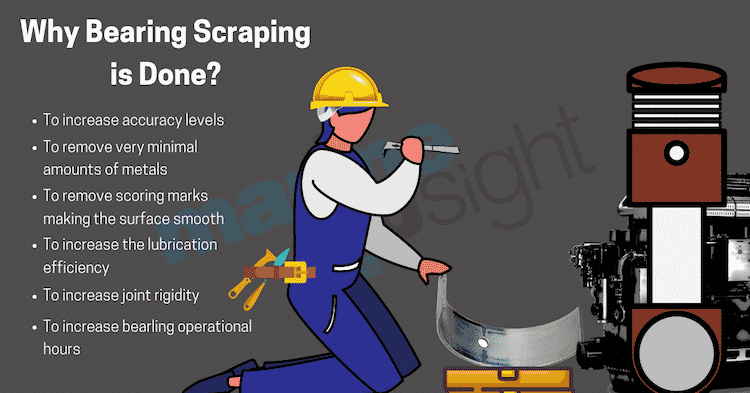
Why scraping of marine bearing is needed?
As marine bearing has the most pivotal roles of conducting relative motions, keeping the rotatory machinery aligned, maintenance is of the utmost importance.
Scraping is the key to maintenance when it comes to marine bearings and scrapping of marine bearings is essential for the following reasons:
- To increase accuracy levels with advancements in process control and machine stiffness.
- To remove very minimal amounts of metal from a precision surface and eliminate high spots caused by the rapid fluctuation of cyclic load on bearings during high speeds and cast a smooth surface out of it so that the bearing is cleaned, well lubricated and perfectly shimmed up such that other rotatory counter-parts is held firmly.
- To ensure easy mounting of machinery components by providing a flat and accurate bearing surface.
- To increase joint rigidity in the machine tools by increasing the bearing contact area between the mating surfaces.
Related eBooks:
Construction and Types of Scraper Tools
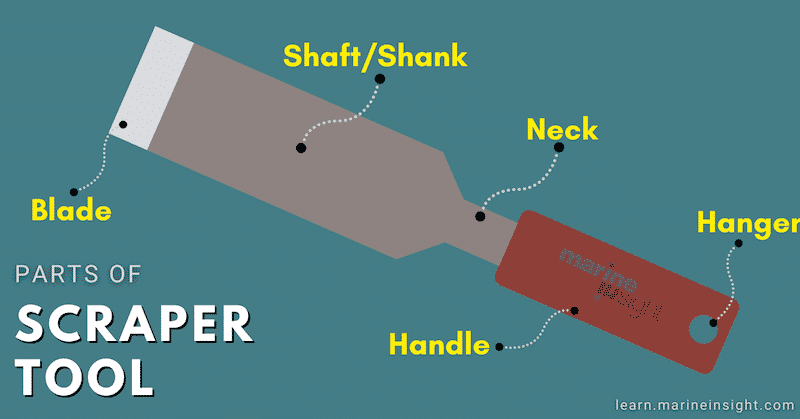
The basic construction of a scraper consists of:
Hanger: A small hole in the upper body of the scraper that is meant for placing the tool upright in the kit room or the designated area.
Handle: The handle starts from the top and follows till the edge of the shaft is generally made up of wood usually circular in shape to provide grip and facilitate handy and easy operation.
Shaft/Shank: This is the longitudinal cylindrical metallic part generally made of hardened or tempered steel which starts at the periphery of the handle and leads to the blade.
Blade: The lowermost operating part of the scraper is the blade whose shape may be triangular, curved as per the desired type of scraping and the scraper.
Types of Scrapers
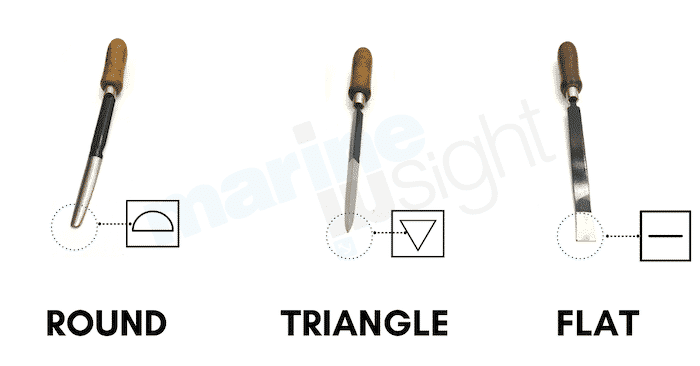
In general, there are mainly three types of scrapers:
Flat or chisel type scraper: This type of scraper is also called the end scraper and looks like a chisel. It comes with sharp and slightly rounded ends aimed at the corner’s operation and debarring the corners to touch the working or mating surfaces and leave scratches.
Triangular Scraper: A triangular scraper, generally made up of bronze or a white metal has a triangular blade with three corners running to a common point. At the tapering end of blades, the edges of the blades are not perfectly straight but rather curve slightly. Their typical use is to deburr holes or the internal surfaces of bush-type bearings.
Curved scraper: A curved scraper is incorporated with relief on its bottom and an integral shank fitted with the handle made of wood to provide grip. This type of scraper has a curved blade and two cutting sharp edges culminating in a rounded end or a point and they are not generally used to dig out deep pockets of Babbit or soft metals of an engine bearing while it facilitates light scratch even in thin areas of an engine bearing, crankshaft main journal bearings or rod bearings.
This type of scraper is generally used in bearing operation.
How bearing scraping is done?
The preparations that should be done before scraping:
- We should not attempt to scrape off three or four-thousandths of an inch of metal on a large surface.
- High spots should be identified before scraping through test fitting and once the camshaft bearings have been changes, test fitting could be done by rotating the camshaft once.
- The surfaces that are to be made flat should be checked against the surface plate and in case of bearing; as it is a curved surface, it must be checked against its mating surface.
- The surfaces that are to be scraped and the reverence surface should be perfectly cleaned.
- A thin film of Prussian blue should be applied on the reverence surface and the high spots could be determined by lightly rubbing the work against the blued reference surface which would determine the areas to be scrapped.
- Visible burrs should be removed before scraping with the aid of files.
Use of scraper or methodology of scraping:
- The bearing scrapers generally have positive contact angles. To use the bearing scraper, we should rest the left wrist on the work or the vice if the workpiece is mounted on it.
- We should use a movement from the wrist or pulling with the left hand and et the blade slide over the workpiece while scraping it. This is how a grip should be imparted on the designated surface.
- When it is not possible to use two hands in close support, one must switch to the scraping tools with a negative contact angle to prevent digging in and chatter.
- After determining the areas to be scraped and the job done by curved bearing; we should then rematch the work to the reference surface until the work surface is covered uniformly with the coating of blue.
Care of scraping tool
- Scraping tools are hand-fledged small tools that need to be taken care of for the scraping needs precision as it is responsible for delivering true surfaces.
- The scraping tools should not be kept along with spanner or filers. Rather, we should keep them in oiled rags to protect their cutting edges from damage.
- Sharpening of the scraping tools should be done on the regular basis to maintain precision.
- Sharpening should be done in a way such that firstly it is grinded on the bottom on the flat face of a smooth grinding wheel and then hand-honed or oilstone it to a fine edge.
- Honing out the grinding marks is of the utmost importance as the irregularities on the blades and ragged cutting edges tend to score the work surface.
You might also like to read:
- Types of Main Bearings of Marine Engines and their Properties
- Procedure for Removing Main Bearing of MAN B&W MC-C Engine
- Understanding Turbocharger Bearings and Lubrication On Ships
- Ways to Measure Main Bearing Clearance of Marine Engine
- Important Points for Checking Ship’s Main Engine Bearings
Disclaimer :
The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data or profits arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this website.
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Disclaimer :
The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data or profits arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this website.
Latest Marine Technology Articles You Would Like:
- 10 Harmful Effects Of Impure Air On Ship’s Machinery
- 10 Important Things to Check While Starting Fuel Oil Purifier on Ships
- 10 Noteworthy LNG-Powered Vessels
- 10 Points for Efficient Turbocharger Operation On Ships
- 10 Practical Tips to Handle Engine Room Pumps
- 10 Precautions to Take Before Operating Controllable Pitch Propeller (CPP) on Ships
Subscribe To Our Newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.