The Ultimate Guide to Tug Boats: Types, Functions, and Applications
A tug, or more commonly a tugboat, is an assistance boat which helps in the mooring or berthing operation of a ship by either towing or pushing a vessel towards the port.
A tug is a particular class of boat which helps mega-ships enter or leave a port. In addition to towing the vessel towards the harbour, tug boats can also be engaged to provide essentials, such as water, air, etc., to a vessel.
Tug boats are also essential for non-self-propelled barges, oil platforms, log rafts, etc. Due to their solid structural engineering, tugs are small but relatively powerful machines.
Their propulsion system is the main reason behind their enormous strength. Some secondary functions of a tug boat, along with easing mooring operation, are listed below:
- They can work as salvage boats and icebreakers.
- They can also have fire fighting accessories to assist in port or barges.
- They are the most critical marine vessels, acting as saviours to ships in hard times, such as in narrow canals and lousy weather.
Most tugboats can also venture into the ocean, but some do not have that propulsion power, like river tugs. River tugs are towboats designed to help out in rivers and canals. Their varied hull types make it dangerous for them to venture into the open ocean.
Renowned tugboat builders include Ranger Tugs, Florida Bay, American Tug, Nordic Tug and Tugboat. They make inboard, outboard, outboard-4S, and other diesel and gas fuel propulsion systems.
Tug boats are known for their moderate draft and broader beam, making them suitable for various commercial and recreational boating activities in coastal, inshore and offshore locations. Tugboats can carry about 6 to 8 passengers or guests.
Applications Of A Tug
The usage and functions of tugs vary from port to port, as different ports have different requirements and intakes. The common thing is pushing or towing mega boats or barges. Their usage depends on the following factors:
- Port traffic volume,
- Types of ships to be served by that tug,
- Navigational obstacles to be catered to,
- Conditions of environmental protection,
- Local laws and
- Domains to be carried by a tug
The tug boats were among the first to have a steam propulsion engine, which the diesel engine has replaced today.
An average tug boat has 680-3400 horsepower engines (500-2500 kW), but those which are larger and venture out into deep waters have engines with a power close to 27200 hp (20000 kW) and a power: tonnage ratio ranging between 2.20-4.50 for large tugs and 4.0-9.5 for harbour tugs. These are incredibly high ratios, especially considering the ratio of cargo ships or vessels varies between 0.35 and 1.20.
Since a tug boat’s manoeuvrability is one of its assets, all engine developments have focused on improving it without compromising the vessel’s strength and power over the years. Thus, the transition from paddle wheels to propellers.
Classification Of Tugs Based on Purpose
Based on purpose, they serve marine tugs can be of two types:
1. Escort Tugs: The tugs designed generally to escort and manoeuvre ferries and barges to their destination are known as escort tugs.
2. Support Tugs: These tugs provide support services for offshore and towing operations. These tugs play a significant role in berthing operations.
Mainly, tugs used in the marine industry are of three types, which are listed:
- Conventional tug
- Tractor tug and
- Azimuth stern drive tug
1. Conventional Tug
These are the tugs we have been using since the start. They are made using the oldest known principle of tug development. The conventional tug has less manoeuvring capability but is still used in almost all ports worldwide.
With technological advancements, tugs are fitted with diesel engines with either one or more propellers. Single propeller tugs are classified into right-handed conventional and left-handed conventional tugs.
Right-handed conventional tugs are more common and likely to be used than left-handed ones. These are highly reliable.
The essential components of conventional tugs are briefed as follows:
- These have a classic rudder.
- A towing hook is provided in the centre of the tug. Along with other components of tug positioning, a hook is of enormous importance. The safety and performance of the tug boat mainly depend on the towing point location. When a gob line accompanies the towel hook, this point can be taken towards the aft; its distance is reduced from its original value of 0.45 times LWL to minimise tug manoeuvring.
- Its stern consists of the power plant complex.
Configuration of propeller used
Screw propeller — In the “conventional” tugboat, the propelling device is generally diesel driven. The propeller develops thrust in water and is responsible for ships’ movement. These tugboats are designated based on several propellers in them:
- Single screw tug implies one conventional propeller tug,
- Twin-screw tug implies a two-propeller traditional tug and
- A triple screw tug implies three classic propeller tugs.
In conventional screw propeller tugs, a moveable nozzle and rudders are provided, but the whole propeller is immovable or fixed.
Advantages
The main advantages or features of conventional tugboats are as follows:
- The construction of traditional tugs is quite simple and requires less maintenance, so the maintenance and construction costs of these tugs are meagre compared to the two types of tugs.
- These are self-sufficient and thus require no support system.
- The smaller the propeller, the larger the open water.
- These tugs have the upper hand and maximum efficiency in towing for port-to-port.
- These assist with pushing and tugging operations while carrying towing on a line.
- The operation cost is relatively low and economical while working with moderate-sized vessels.
Disadvantages
There may be certain disadvantages of conventional tugboats, and these are briefed as follows:
- The design principle is ancient; thus, it degrades performance standards.
- They are unidirectional and cannot work in the reverse direction until provided with a reduction gear to facilitate reverse flow.
- There are more chances of cavitation in these tugs.
- These tugs’ stability and strength are less than the other two.
- Due to obsolete design principles, their usage is limited to small and medium boats, so azimuthal stern drive and tractor tugs are employed to assist the mega ships.
- The repositioning of the tugs is relatively slow due to the limited manoeuvring capacity.
- There are more chances of capsizing or overturning the vessel, which results in fatal accidents. A release hook is required to overpower this issue of capsizing and halting the development of girthing.
- Conventional tugs have low values of astern power
2. Tractor Tug
The key to the tractor lies in using a 2-multidirectional propulsion unit, some of which are like large rotating outboard motors, with others consisting of rotating vertical blades.
They enable the tug’s thrust units to be placed side by side, more or less under the bridge, facilitating spectacular manoeuvrability in the right hands.
The towing point can be placed much nearer the stern to get maximum output from the propulsion units, and therefore, the thrust is always outside of the towing point, thus creating a joyous turning moment.
The rotating disc decides the magnitude of the force of thrust. Tractor tugs’ versatility is further enhanced by working the tug’s towline directly from a winch drum with a remote joystick controlled from the bridge. The tug master can thus alter the span of the towline at his will and with considerable ease. Their precision in manoeuvring makes them the most widely used tugs.
Advantages:
It is the most critical type of tug, and a tractor tug has many positive points. Some of its advantages are briefed as below:
- These are the only tugs which provide full thrust over 360 degrees.
- They have rapid power-on response time and are well known for their outstanding manoeuvrability.
- In contrast to conventional tugs, tractor tugs are adaptable to repositioning swiftly at the pilot’s will or on demand of the towing job in which they are employed. Thus, they are readily available tugs with high-efficiency values.
- Their straightforward control systems pose a shallow risk of girthing or capsizing.
- These have extraordinary performance and fast speed.
- They can effectively overcome the forces of interaction with ships at close distances.
- They can work efficiently in sideways movement due to the close location of the propulsion unit to the turning point.
- They have improved operational capability in restricted areas such as a lock flow channel.
- In these types of tugs, a rudder is not required, and the use of a rudder can be eliminated.
- They have reliable and robust propulsion units.
Disadvantages
Tractor tugs are the most effective and potent sort of tugs. As everything has specific cons and pros, these have certain loopholes, mainly their complexity and cost. Other drawbacks of these tugs are as follows:
- These kinds of tugs have less bollard pull than ASD tugs.
- They are considered to have very high capital investment costs, implying a lot of money is required to buy and maintain these tugs. In short, it confers that the initial and maintenance cost of tractor tugs is very high.
- The repair and maintenance of complex under-water units of these tugs are pretty expensive
- Handling in an open seaway might be poor with the short distance between the pivot point and the thrust creating a short turning lever
- Heeling angles with full side thrusts may be up to 21 degrees with some tugs. Therefore, the risk of damage can exist when lying alongside a ship
- Sophisticate under-water units may be damaged on grounding
- A draft may be up to 5m, which is significant in comparison to conventional tugs
- The retraining of a traditional tug master is essential to maximise a tug’s potential fully
3. Azimuthal Stern Drive (ASD) Tugs
These tugs are midway between conventional and tractor tugs as these utilise some of the benefits of both traditional and tractor pulls. It can have two towing locations, one forward and one amidship, and the main propulsion is from two rotating azimuth units, which are placed like a traditional twin screw tug.
Advantages
These are considered more efficient than conventional tugs but less efficient than tractors. The significant advantages of using ASD tugs are as follows:
- Better directional stability at speed
- They are more suitable hull form for open waters and working in a seaway
- They have improved the bollard pull
- The azimuth units are easy to withdraw for maintenance and repair
- The maximum heel with side thrust is less than 15 degrees, compared to tractor tugs, which have a twenty-one-degree value.
- These tugs have a shallower average draft of 3m
Disadvantages
These tugs are challenging to work with as compared to tractor tugs, and other drawbacks of working with these tugs are as follows:
- The side-stepping ability of ASD tugs is not so good.
- The squat at the stern and flooding of the aft deck have been acquainted with certain types when backing with full power.
- They are still susceptible to girting or capsizing when using the aft towing position.
- These types of tugs are slightly more at risk from the interaction effects.
- These have somewhat Complex control systems.
- These tugs are more susceptible to rubbish damage in propellers
- It is not uncommon for 99 % of all towing to be limited to a forward position
Other Miscellaneous Types Of Tugs
Along with these classifications mentioned above, some other miscellaneous types of tugs are briefed as below:
1. Tractor Tugs With Cycloidal Propellers
Before the Second World War, tugboats had high power ratings and large tonnage capacities, and the propeller used was cycloidal to facilitate manoeuvrability; these were renowned as Cycloidal Tugboats. Voith Schneider propeller (VSP) is an advancement of a cycloidal drive. It is excellent at manoeuvring operations, so it became a perfect choice for ferries and barges.
2. The Carousel Tug
The Dutch developed the Carousel Tug, which emerged as an award-winning Maritime innovation in 2006. It consists of interlocking inner and outer rings, the former connected to a vessel and the latter with the tug’s body attached to a towed ship through winches or hooks.
3. Reverse Tractor Tugs
The tractor tugs are termed reverse tractor tugs if they have Z-drive aft-mounted propulsion units. These reverse tractor tugs don’t have a skeg and work efficiently in escorting. These tugs have fewer fatigue issues than tractor tugs due to the unavailability of flat plate skeg. Generally, ASD tugs serve as reverse tractor tugs.
4. Combi-Tugs
A bow thruster and a nozzle with steering are fitted with a conventional Screw Tug to improve manoeuvrability. These modified tugs, along with additional devices like a thruster and steered nozzle, equipped with the latter devices are referred to as “Combi-Tugs”. Combi-Tugs are preferably modified with twin-screw conventional tugs to have maximum efficiency.
5. Z-PELLER
It can have two towing locations, one forward and one amidship, and the main propulsion is from two rotating azimuth units, which are placed like a traditional twin screw tug. Azimuthing propulsion unit replaces conventional shafts and propellers, which allows 360-degree rotation about the vertical axis.
6. Giano Tug
The Giano Tug is highly stable and can serve the purpose of both support and escort tug. It is a high-tech tug which allows remote manoeuvring through VSAT or 4G connections. Its 360-degree rotation and excellent side-stepping speed made it to the top in the order of standards of tugs.
7. Eco-Tugs
Hybrid technology tugs or tugs with LNG as a running fuel are categorised as eco-tugs. These tugs serve the same purpose of escorting and supporting as the conventional tugs, but without harming and polluting the marine ecosystem.
8. Ice Tugs
These tugs escort ferries or barges and serve as icebreakers or salvage boats to make the ferries and barges speed up to their destination.
The Most Powerful Tug in the World
“The title of most powerful tugboat crowns Farstad Shipping’s Far Samson by the Guinness World Record, which achieved an astounding four hundred twenty-three tons bollard pull during testing.” The Spanish shipyard launched a groundbreaking, powerful tug boat to supply the Luleå, Sweden Port.
But presently, Gondan Shipyard promises to build and deliver an ice-breaking towing tug, which is assumed to bag the ticket for the most potent hybrid tug in the World.
Robert Allan’s design was the foundation for building this tug. To assist ships or vessels through challenging regions, it employs a powerful hybrid power system, namely Wärtsilä’s HYTug power system. It combines “Lloyd’s Register class and a 3600-H design of RAL TundRA”.
All the super, as well as substructures of this giant, are very strong and efficient. The superb hull structure is provided, which beats even the class rules of Finnish-Swedish ice. The excellent bollard pull of this tug of about 100 tonnes emphasised its capabilities. It is operated in a diesel manual mode to achieve maximum efficiency.
These can easily break a metre of ice with a comparatively high speed of about three knots. The tug’s thirty-six-metre span is equipped with an excellent propulsion system. Its propulsion system comprises batteries to store energy and run in specific emergencies, shaft motors, generators, two diesel key engines, etc.
The essential features of this tugboat are as follows:
- It is flexible in operation and can switch swiftly.
- It emits less fuel under its hybrid conformations, making its maintenance economical and more accessible.
- There are a variety of operation modes available in this tug due to its innovative and hybrid design.
- It can serve multi-purpose purposes in ice management, assisting ships and enormous barges during voyages, fighting fires, and towing in coastal regions and difficult conditions.
You might also like to read:
Disclaimer: The author’s views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of Marine Insight. Data and charts, if used, in the article have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and Marine Insight do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendations on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and Marine Insight.
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Latest Type Of Ships Articles You Would Like:

About Author
Zahra is an alumna of Miranda House, University of Delhi. She is an avid writer, possessing immaculate research and editing skills. Author of several academic papers, she has also worked as a freelance writer, producing many technical, creative and marketing pieces. A true aesthete at heart, she loves books a little more than anything else.
Subscribe To Our Newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.
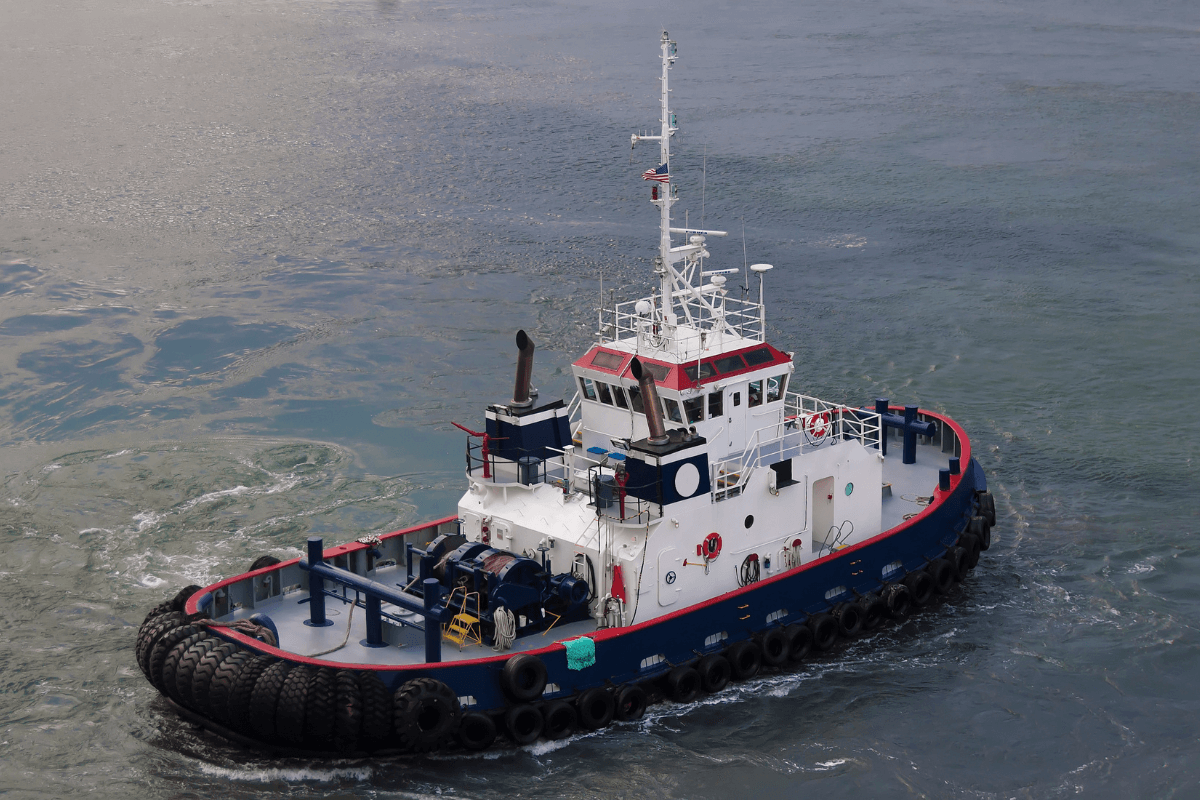
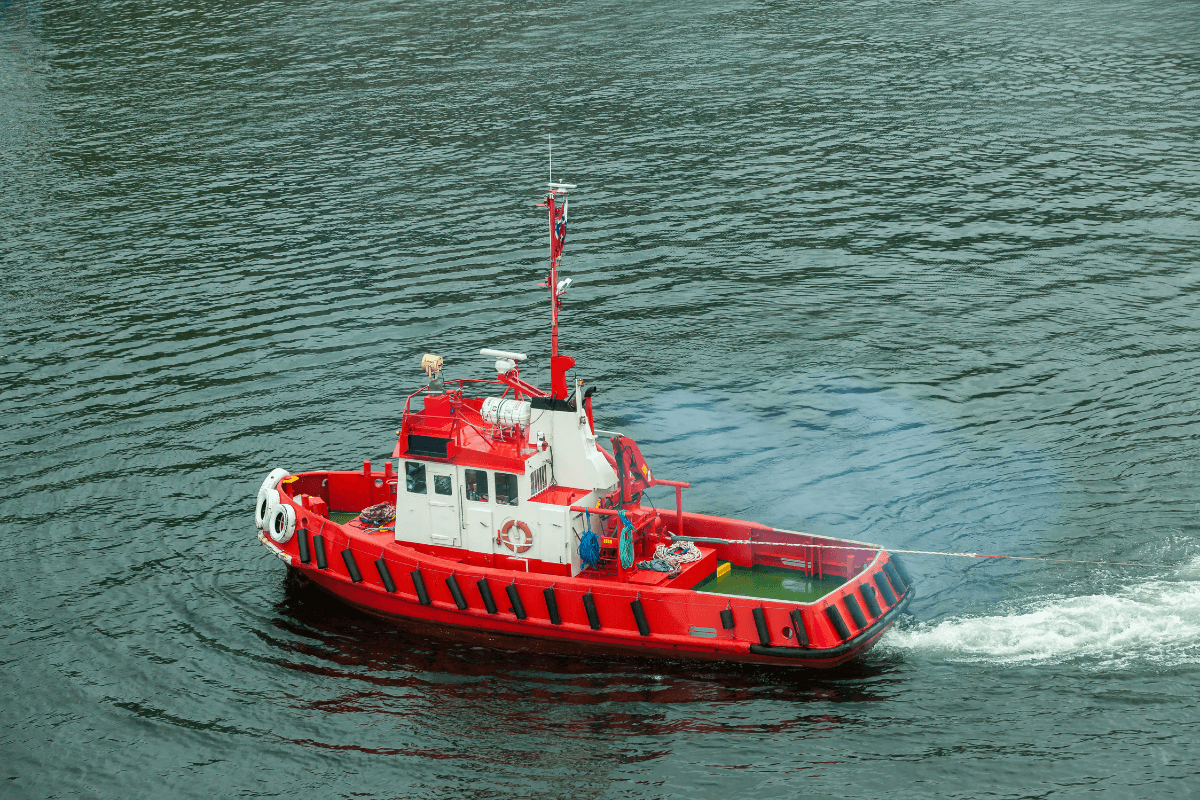




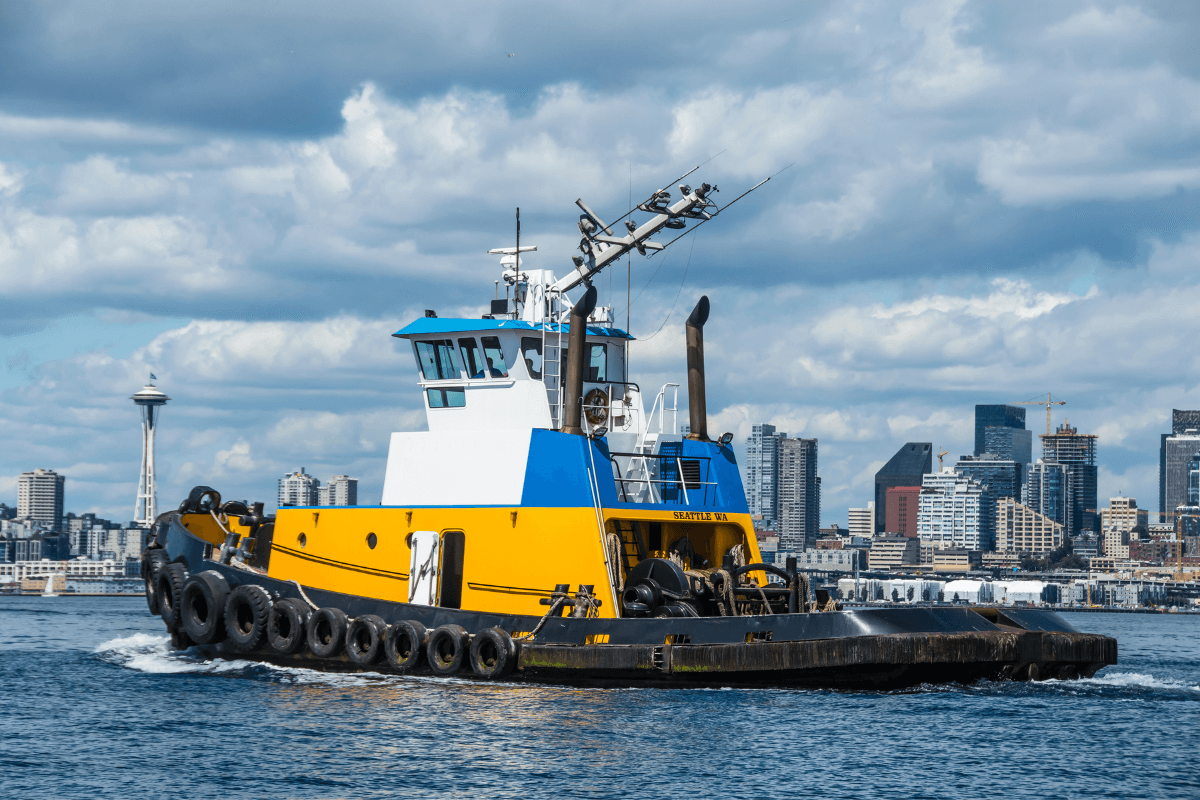


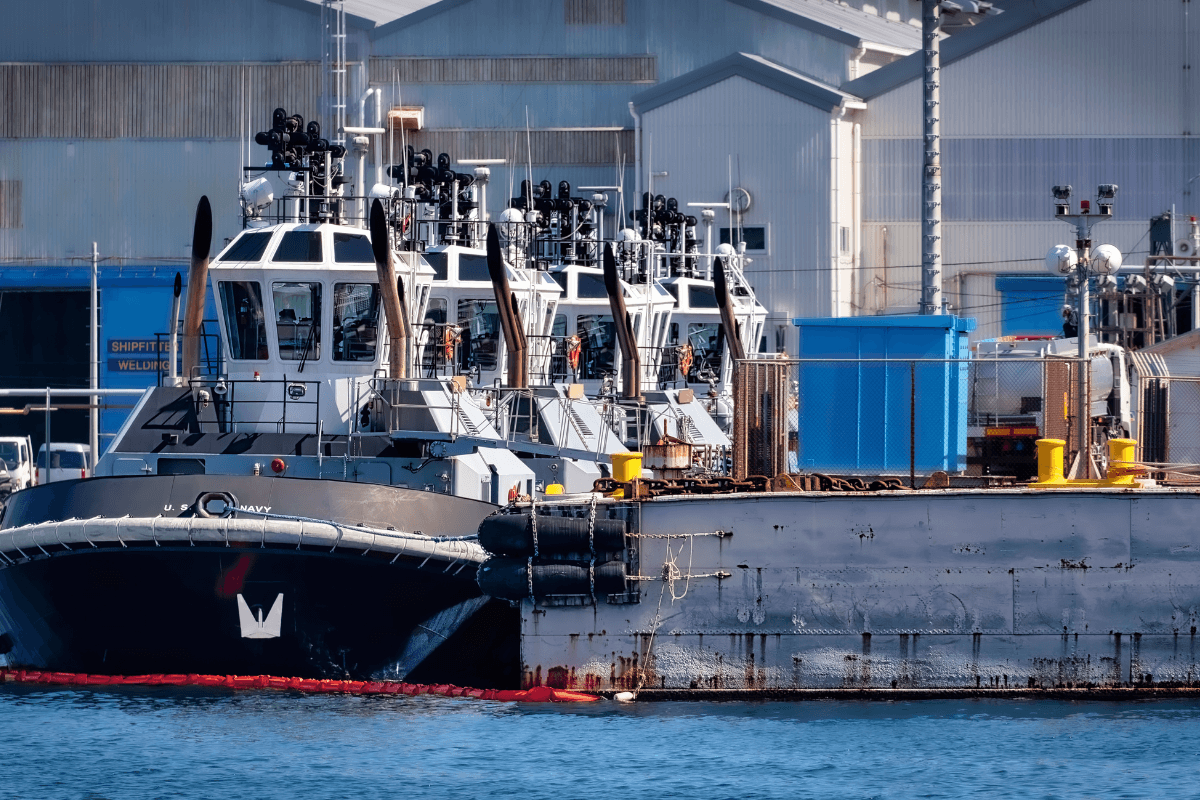









Not only a dirty job, but one of these most dangerous too. They work with cables that are under huge amounts of strain and could snap. Hat tip to all the tug boat crews out there, helping ships in their time of need.
I am engineer Ali Abusada from Libya I was the chairman of Libyan to wage and selvage company now I am consulting engineer for the company , we are looking for getting new tugboats of 5000hp 4500 hp 300 hp.
I need to know where we can find chance in Mediterranean