How Ballast Water Treatment System Works?
Invasive Aquatic Species in ship’s ballast water is one of the biggest problems faced by the shipping industry. Posing a great threat to the marine ecosystem, these aquatic species has led to an increase in bio-invasion at an alarming rate.
Under IMO’s “International Convention for the Control and Management of Ship’s Ballast Water and Sediments”, the implementation of a ballast water management plan and ballast water treatment system on board ships has thus become important.

In order to ensure their ships comply with the rules and regulations set by IMO regarding Ballast Water Management, several shipping operators have started implementing ballast water treatment systems on their ships.
A variety of technologies are available in the market for treating ballast water on ships. However, constraints such as availability of space, cost of implementation, and level of environmental friendliness play an important role in the usage of a particular type of ballast water treatment system.
A number of factors are taken into account for choosing a ballast water treatment system for a ship. Some of the main factors taken into consideration are –
- Effectiveness on ballast water organisms
- Environment-friendliness
- Safety of the crew
- Cost-effectiveness
- Ease of installation and operation
- Space availability on board
The main types of ballast water treatment technologies available in the market are:
- Filtration Systems (physical)
- Chemical Disinfection ( oxidizing and non-oxidizing biocides)
- Ultra-violet treatment
- Deoxygenation treatment
- Heat (thermal treatment)
- Acoustic (cavitation treatment)
- Electric pulse/pulse plasma systems
- Magnetic Field Treatment
A typical ballast water treatment system onboard ships use two or more technologies together to ensure that the treated ballast water is of IMO standards.
Physical Separation/ Filtration Systems Ballast Water Treatments
Physical separation or filtrations systems are used to separate marine organisms and suspended solid materials from the ballast water using sedimentation or surface filtration systems. The suspended/filtered solids and waste (backwashing) water from the filtration process is either discharged in the area from where the ballast is taken or further treated onboard ships before discharging.
The following equipment is mainly used for ballast water filtration:
Screens/Discs: Screens (fixed or movable) or discs are used to effectively remove suspended solid particles from the ballast water with automatic backwashing.
These are extremely environmentally friendly as they do not require the usage of toxic chemicals in the ballast water. Screen filtration is effective for removing suspended solid particles of larger sizes but is not very handy in removing particles and organisms of smaller sizes.
Note: It has been noticed that though screens are highly effective in removing the majority of suspended solid particles and organisms from ballast water, they alone are not sufficient to treat the ballast water according to IMO standards.
Hydrocyclone: Hydrocyclone is effective equipment for separating suspended solids from ballast water. High-velocity centrifugal force is used to rotate the water to separate solids. As hydrocyclone doesn’t have a moving part, it is easy to install, operate and maintain onboard ships.
Note: It has been found that as the operation of hydrocyclone heavily depends on the mass and density of the particle, they are not successful in removing smaller organisms from the ballast water.
Coagulation: As most of the physical filtration methods are not able to remove smaller solid particles, the method of coagulation is used prior to the filtration process to join smaller particles together to increase their size. As the size of the particles increase, the efficiency during the above-mentioned filtration processes increases. Such treatment involving coagulation of smaller particles into small flocs is known as flocculation. The flocs settle more quickly and can be removed easily.
Note: Some ballast water treatment systems using coagulation and flocculation utilize ancillary powder (sand, magnetite etc.) or coarse filters to produce flocs. An additional tank is required for treating ballast water for this process and thus extra space is required onboard ships.
Media Filters: Physical ballast water treatment systems with media filters can also be used in order to filter out smaller sized particles. It has been found that compressible media filters (Crumb rubber) are more suited for shipboard use because of their compact size and lower density as compared to conventional granular filtration systems.
Magnetic Field Treatment
The magnetic field treatment uses coagulation technology. Magnetic powder is mixed with the coagulants and added to the ballast water. This leads to the formation of magnetic flocs which includes marine organisms. Magnetic Discs are used to separate these magnetic flocks from the water.
Chemical Disinfection (Oxidizing and non-oxidizing biocides) Ballast Water Treatments
Biocides (Oxidizing and non-oxidizing) are disinfectants that have been tested to potentially remove invasive organisms from ballast water.
Biocides remove or inactivate marine organisms in the ballast water. However, it is to note that the biocides used for ballast water disinfectant purposes must be effective on marine organisms and also readily degradable or removable to prevent discharge water from becoming toxic in nature.
On the basis of their functions, biocides are mainly divided into two types:
- Oxidizing
- Non-Oxidizing
Oxidizing biocides: Oxidizing biocides are general disinfectants such as chlorine, bromine, and iodine used to inactivate organisms in the ballast water. This type of disinfectant act by destroying organic structures of the microorganisms such as cell membrane or nucleic acids.
Non-oxidizing biocides: Non-oxidizing biocides are a type of disinfectants which when used interfere with the reproductive, neural or metabolic functions of the organisms.
More information on biocides can be found here.
Oxidizing Biocides
Some of the processes utilizing oxidizing biocides used onboard ships are:
Chlorination – Chlorine is diluted in water to destroy the micro-organisms.
Ozonation – Ozone gas is bubbled into the ballast water using an ozone generator. The ozone gas decomposes and reacts with other chemicals to kill organisms in the water.
Other oxidizing biocides such as chlorine dioxide, peracetic acid, and hydrogen peroxide are also used to kill organisms in the ballast water.
Non-Oxidizing Biocides
Though there are several non-oxidizing biocides available in the market, only a few such as Menadione/ Vitamin K are used in ballast water treatment systems as they tend to produce toxic by-products. A lot of research is being made in this field to make more non-oxidizing biocides feasible for use in ballast treatment plants.
Ultra-Violet Treatment Method
The ultraviolet ballast water treatment method consists of UV lamps that surround a chamber through which the ballast water is allowed to pass. The UV lamps (Amalgam lamps) produce ultraviolet rays which acts on the DNA of the organisms and make them harmless and prevent their reproduction. This method has been successfully used globally for water filtration purposes and is effective against a broad range of organisms.
De0xygenation
As the name suggests, the deoxygenation ballast treatment method involves purging/removing oxygen from the ballast water tanks to make the organisms asphyxiated. This is usually done by injecting nitrogen or any other inert gas in the space above the water level in the ballast tanks.
Note: It generally takes approximately 2-4 days for the inert gas to asphyxiate the organisms. Thus, this method is usually not suitable for ships having short transit times. Moreover, such types of systems can be used on ships with perfectly sealed ballast tanks. If a ship is already installed with an inert gas system, then a deoxygenation system will not require more space onboard ships.
Heat Treatment
This treatment involves heating the ballast water to reach a temperature that will kill the organisms. A separate heating system can be utilized to heat the ballast water in the tanks or the ballast water can be used to cool the ship’s engine, thus disinfecting the organisms from the heat acquired from the engine. However, such treatment can take a lot of time before the organisms become inactive and would also increase the corrosion in the tanks.
Cavitation or Ultrasonic Treatment
Ultrasonic energy is used to produce high energy ultrasound to kill the cells of the organisms in ballast water. Such high-pressure ballast water cavitation techniques are generally used in combination with other systems.
Electric Pulse / Plasma Treatment
The electric pulse /plasma for ballast water treatment is still in the development stage. In this system, short bursts of energy are used to kill the organisms in ballast water.
In pulse electric field technology, two metal electrodes are used to produce energy pulse in the ballast water at very high power density and pressure. This energy kills the organisms in the water.
In electric plasma technology, a high energy pulse is supplied to a mechanism placed in the ballast water, generating a plasma arc and thus killing the organisms.
Both these methods are said to have almost the same effect on the organisms.
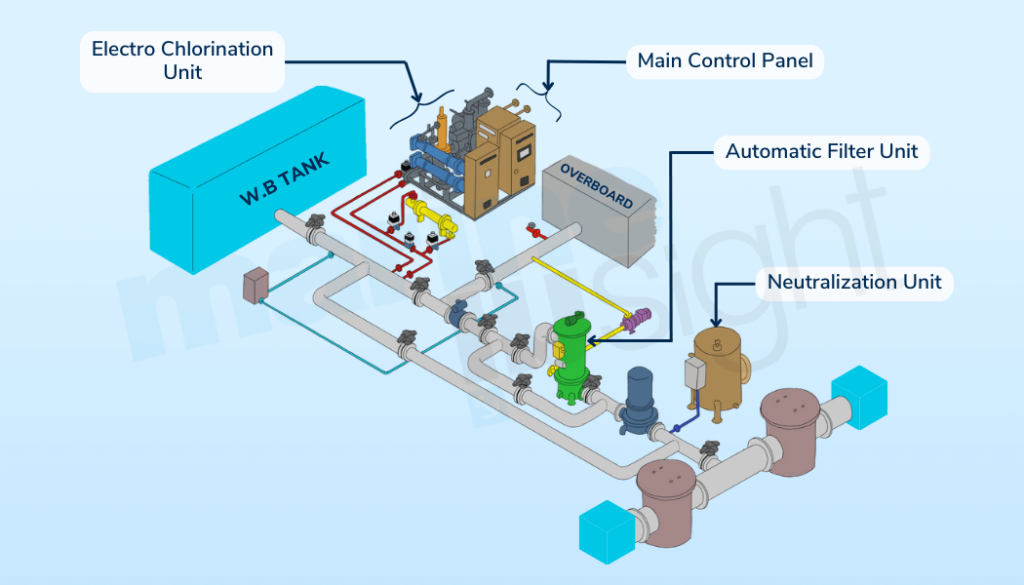
A Typical Ballast Treatment Treatment System on Ships
Most of the ballast water treatment systems use 2-3 disinfectant methods together, divided into different stages. A general ballast water treatment plant comprises two stages with one stage using physical separation while the second stage employing some disinfectant technology. The choice of treatment system used in combination depends on a variety of factors such as type of ship, space available on the ship, and cost limitations as mentioned before.
A typical ballast water treatment system on ships looks like this:
Several new technologies to ballast water on board ships are entering the market every month. Do you know any new and promising technology to treat ballast water? Let us know in the comments below.
Additional References: Ballast water management: Understanding the regulations and various treatment technologies
Disclaimer :
The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data or profits arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this website.

About Author
Raunek Kantharia is a marine engineer turned maritime writer and entrepreneur. After a brief stint at the sea, he founded Marine Insight in 2010. Apart from managing Marine Insight, he also writes for a number of maritime magazines and websites.
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Disclaimer :
The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data or profits arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this website.
Latest Marine Technology Articles You Would Like:
- 10 Harmful Effects Of Impure Air On Ship’s Machinery
- 10 Important Things to Check While Starting Fuel Oil Purifier on Ships
- 10 Noteworthy LNG-Powered Vessels
- 10 Points for Efficient Turbocharger Operation On Ships
- 10 Practical Tips to Handle Engine Room Pumps
- 10 Precautions to Take Before Operating Controllable Pitch Propeller (CPP) on Ships
Subscribe To Our Newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.









Hi
Electrocatalysis and Ozone injection type of treatment can be added
We are patent holders and manufacturers of Nano bubble technology..This is a very high potential treatment solution for Balast water….We can input any gas through our system like ozone and because of its high dissolution rate which is upto 95 percent compared to existing 20 percent not only helps it use Ozone and oh ( hydroxyl radicals, which is 2000 times more powerful than chlorine) to disinfect but also rapidly floculate suspended solids and float it on surface to easily skim it….There fore both can be done with one system reducing footprint substantially and disinfecting water upto 99.8 percent.very fast.
Dear Sirs,
It is appalling to see how many educated adults are promoting the deadly business of ballast water. Remember, bad publicity is good publicity.
Simple laws of physics confirm that water is inefficient ballast, it works only above waterline. Not to waste your time, here is I.P. of available technology eliminating ballast water entirely and radically improving safety of navigation at the same time.
Eliminates water as a ballast, is 7 times more efficient;
It works simultaneously by applying gravity and buoyancy, in real-time;
Mitigates roll, some pitch, prevents accumulation of parametric roll, the most deadly phenomenon;
Fully autonomous, not affected by human error;
Independent of electricity, sensors, servo-gears;
Balances ship while loading and under way;
Can correct, within a range, draft;
Is configurable;
Stability is enforced in both cases of wave caused disturbance and shift in cargo, e.g. when a thousand vacationers rush to one side of ship ‘to see whales’. Such intervention requires actions in contradicting directions. No Architect, to my knowledge, has even attempted to solve this problem;
All these functions are accomplished by a single technology.
Research Insights : The global ballast water treatment systems (BWTS) market is expected to reach USD 117.55 billion by 2025, driven by growth in the size of shipping industry trade volume and rising government initiatives in line with the International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations.
Companies are actively looking for new ballast water treatment projects alongside investing in R&D to enhance technology.
Additional knowledge in ballast water treatment method.
kindly be inform that we have two vessels:
West scent imo no. 9132703
Noble breeze imo no. 9126871
We are looking for bwms.
Appreciate if you advise the suitable system for our vessels as well as the cost.
its interesting topic and its critical
MY freind bought like an auction and that device was
online Chlorine and TRO Monitor , can you please explain more about this device
its From HF SCIENTIFIC
thanks
Appreciate an answer
thanks