Hydraulic Starting of Emergency Generator
Maintaining continuous power on the ship is one of the most important tasks while sailing. However, sometimes accidents are inevitable and due to some reason such as a breakdown of machinery, technical snag etc. there can be a power failure on the ship.
During such conditions, emergency equipment like life boat, navigation lights etc. should be in operating conditions so that they can be used in case of emergencies. As we all know that a ship is built underclass regulations and all the necessary regulation described by SOLAS and IMO have to be followed during the construction of the ship.
In case of blackout there should be an alternate source of power available and which should come on load automatically. The alternate source of power is taken from batteries and emergency generators to provide power to critical equipment. As batteries cannot provide power for a longer period of time, emergency generators are preferred.
Understanding Emergency Power System
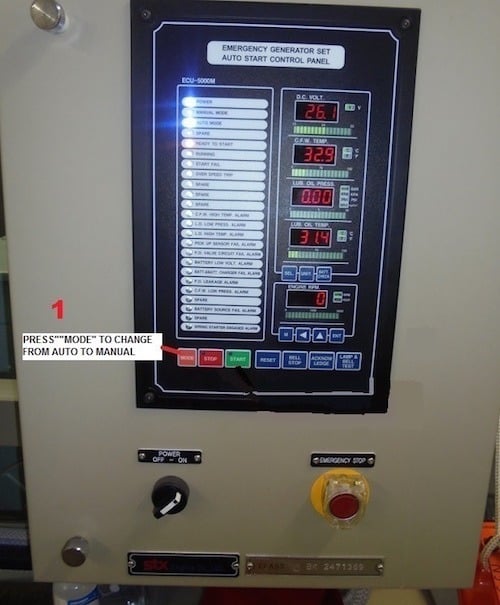
As per SOLAS regulation the emergency power equipment should come on load within 45 seconds of the power failure. When the power failure takes place the emergency generator is normally started by a small electric motor which cranks the engine for starting. This motor gets power from the battery which is being charged by emergency switchboard. Also in case the equipment or emergency generator is unable to start due to any reason, there should be an alternate method or manual starting available in hand. As per Solas regulation, the secondary means of starting should be able to provide additional three starts within 30 minutes.
One of the most common methods for starting emergency generator is hydraulic starting. Options other than hydraulic start are:
1) By compressed air.
2) Inertia starters.
3) Hand cranking
Construction and Working Principle
Hydraulic system for starting works on the principle of hydraulic and pneumatic, in which, the energy is first stored and then supplied or released for the starting of the engine.
The main components of this system are:
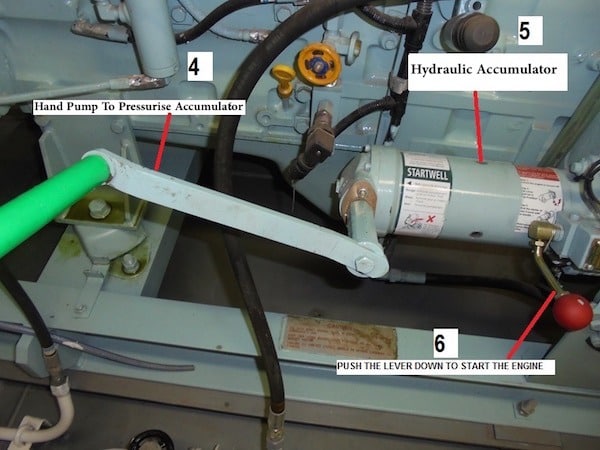
1) Feed tank and hand pump
The feed tank is provided with hydraulic oil which is pumped by the hand pump to the accumulator which helps in starting the engine.
2) Hydraulic Accumulator
This is the most important component of the system. It is the heart of the system where the energy is stored. It consists of a cylinder in which there is a leakproof sliding piston. Above this piston, the cylinder is pre-charged with the nitrogen gas to about a pressure of 200 bars. The oil is pressed against this piston and necessary pressure of oil is stored in the accumulator.
3) Pressure Gauge
This is to check the pressure in the accumulator.
4) Relay valve lever
The operation of this lever will release the energy stored in the accumulator to the starter unit.
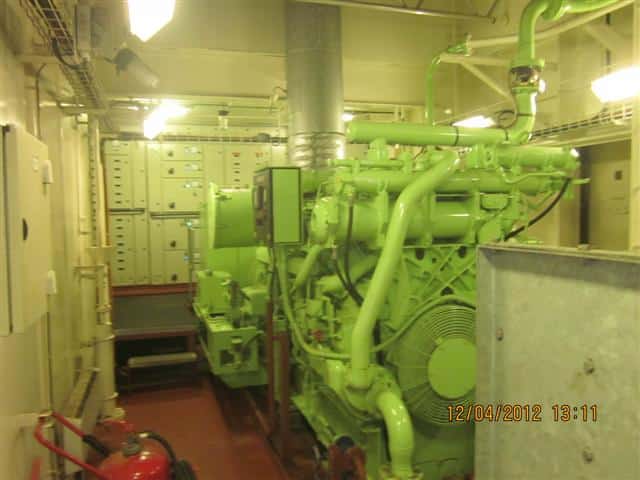
5) Starter unit and engine dog
The starter unit is attached to the free end of the engine with the help of a bracket and the engine dog is attached to the engine crankshaft with the help of a suitable adapter. This starter unit consists of two opposed cylinders with rack and pinion arrangement. The pinion arrangement has teeth on one end which drives the dog having the corresponding teeth. Two helical grooves are formed inside the periphery of the pinion which is engaged by spring loaded balls inside the starter housing which helps in engaging and disengaging by the axial movement. The positive engagement is maintained by the helical tooth form of the pinion and racks.
How to Operate the Hydraulic Starter?
1) Check whether all the valves for fuel, cooling water etc. are open to the generator.
2) Check the level of the feed tank. Fill it if necessary. Please see that if the level in the gauge glass is low and the pressure in the accumulator is ok as per manufacturer recommendation then do not fill the tank as the oil will return from the starter after starting.
3) Check the pressure in the accumulator. Raise pressure if required. Pressurize the accumulator as per OEM recommendations.
4) Operate the relay valve lever. The relay valve lever operates in two stages. Move the relay valve to an angle of 45 degrees, at this position the resistance is felt. In this stage a small bleed is given to the starter causing a slow rotation, engaging the dog. When the dog gets engaged to operate the lever fully. This releases the pressure in the starter and engine starts. The sudden jerk of relay lever is avoided so as to prevent damage to the gears and the clutching arrangement.
5) When the engine starts turning, release the lever and the lever goes back to normal position. The oil used for starting the engines comes back to the feed tank after starting.
6) Check the pressure in the accumulator. It should be enough for two additional starts.
7) Raise the pressure again for the next emergency.
If you liked this article, you may also like Procedure for starting emergency steering system.
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Latest Marine Technology Articles You Would Like:
- 10 Situations When Ship’s Generator Must be Stopped Immediately
- 10 Important Tests for Major Overhauling of Ship’s Generator
- 8 Important Points To Note For Maintenance Of Emergency Generators On Ship
- Understanding Different Operational Modes Of Shaft Generator On Ships
- Ways of starting and testing emergency generator
- What’s The Criteria For Reuse or Replacement of Auxiliary Engine Connecting Rod On Ships?
Subscribe To Our Newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.
Web Stories

About Author
An ardent sailor and a techie, Anish Wankhede has voyaged on a number of ships as a marine engineer officer. He loves multitasking, networking, and troubleshooting. He is the one behind the unique creativity and aesthetics at Marine Insight.











Interesting article but it does only seem to cover the Prestolite/Lucas/Bryce type hydraulic starting system which mount on the end of the crank shaft. There are also hydraulic versions of conventional ring gear starter motors available.
I am researching a source of a hydraulic starter for an old 4 cylinder (1972) Perkins marine diesel.
Thought you might be interested in Hydraulic Starter Availability. Please check out our website
https://hydraulicstarters.ca
Nice information….But I have one dout….why it is specifically 45 seconds…..why it cannot be 60 or more than 60.
Known person plz answer this
Your photo there is misleading, it showing the mechanical starter or most commonly called spring starter. Batteries, spring starter and compressed air starter are the most commonly used in a ship. Your procedure should concentrate more on such starting system.