9 Types of Maritime Crimes
Marine crime is as old as this industry itself. Depending on the times that it prevailed in, the nature of maritime crime has changed a lot over the years but its implications remain just as severe. Marine crime is not only a threat to entire maritime security of goods and people in the industry, but also gives major setbacks to the entire marine industry economically.
Let’s have a look at the various activities termed as Marine Crimes
At present, there are several maritime crimes that exist. They all differ in their execution but the end result remains the same- loss of life and property. Some of these crimes are:
1. Maritime Piracy– Maritime piracy remains one of the biggest crimes of this industry. From causing immense financial loss to causing physical harm to crew members, piracy at sea is probably the most notorious marine crime and a major threat to maritime security.
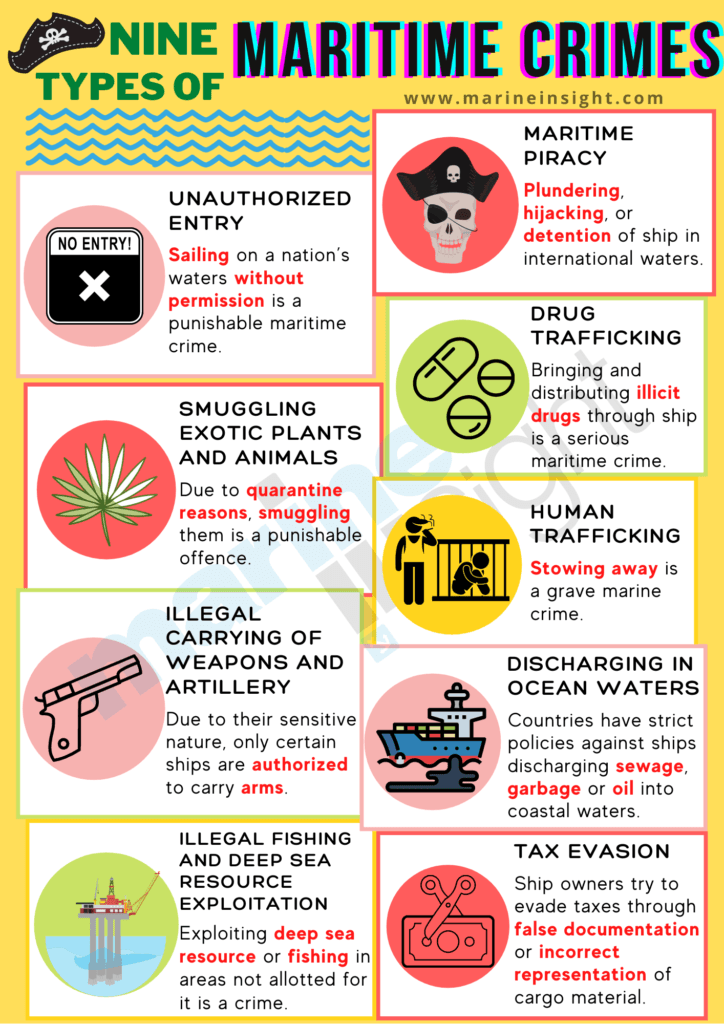
2. Unauthorized entry– For entry of any ship into a nation’s marine boundary, the ship must seek permission from government of that nation. Sailing on that nation’s waters without a permission is a maritime crime and punishable in all countries.
3. Smuggling Exotic plants and animals– Due to quarantine reasons mainly, it is not legal for any ship to bring in exotic plants or animals into a nation without proper permission. Doing so is a punishable offense with punishment ranging from a fine to imprisonment in some cases.
4. Drug trafficking– it is one of the most common types of maritime crime. Bringing in illicit drugs through a ship and their further distribution becomes a serious maritime crime.
5. Illegal Carrying of Weapons and artillery– due to sensitive nature of these goods, only certain ships are authorized to carry arms and weapons even for transportation purposes. Bringing in weapons on a ship not authorized to do so will make it a punishable offense. Also, a ship which is not equipped to handle such materials may be highly prone to maritime accidents along with endangering lives of others around her.
6. Tax evasion– a white collar maritime crime, this is more common than what is told. Cases of ship owners trying to evade taxes through false documentation or incorrect representation of cargo material have been increasing rapidly, posing a threat to maritime security.
7. Sailing or fishing in unauthorized areas– presence of a ship in an unauthorized spot for any purpose what so ever or fishing in areas not allotted for it is a marine crime and punishable by law. Not just that, crimes such as these can often lead to maritime accidents that can become massive very easily.

8. Discharging in Ocean Waters: Marine pollution is a serious issue and almost all countries have strict policies against ships discharging sewage or oil into their coastal waters.
9. Human Trafficking: Cases of stowaways are common in the maritime industry. Travelling to a different country without the permissions from the respective country is a grave marine crime.
Ways to improve maritime security
The above mentioned crimes pose a threat to maritime security on a daily basis. Despite of all the efforts, security of waters still suffers a little. The main reason for that is this is a very broad aspect with no concrete boundaries. Lack of a coherent system with insufficient cooperation between countries is also a reason why these crimes still look marine industry in the face. Some ways through which marine crimes can be combated include:
- Better surveillance
- Use of satellite tracking
- Tighter norms and regulations
- More efficient monitoring of ships and ports
- Better quarantine services
Ships being hijacked or drugs being smuggled into the countries are news more common than what is appropriate. As such, it is important that countries realize the loopholes in their security systems and find ways to thwart them.
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Latest Ship Safety Articles You Would Like:
About Author
Marine Insight News Network is a premier source for up-to-date, comprehensive, and insightful coverage of the maritime industry. Dedicated to offering the latest news, trends, and analyses in shipping, marine technology, regulations, and global maritime affairs, Marine Insight News Network prides itself on delivering accurate, engaging, and relevant information.

About Author
Marine Insight News Network is a premier source for up-to-date, comprehensive, and insightful coverage of the maritime industry. Dedicated to offering the latest news, trends, and analyses in shipping, marine technology, regulations, and global maritime affairs, Marine Insight News Network prides itself on delivering accurate, engaging, and relevant information.
Subscribe To Our Newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.




















Keeping a seaman on board outside his signed contract and against his will,agencies are just keeping mum and saying they are struggling to find a reliever, isn’t this a maritime crime in MLC?
It makes sense that maritime security is so important since there are no concrete borders in the ocean. Making sure that there is a security system in place in the ocean is a good idea. Making sure that the security team you have in place is experienced is important.
if i found captain died on board what should i do or how to report.
First, have an eyewitness about what you have found and you need to inform the company office and nearest coastal authority